Effects of TBBPA Exposure on Neurodevelopment and Behavior in Mice
- PMID: 40806421
- PMCID: PMC12346716
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157289
Effects of TBBPA Exposure on Neurodevelopment and Behavior in Mice
Abstract
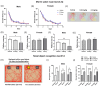
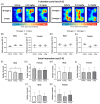
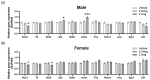
Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) is a brominated flame retardant widely used in consumer products. TBBPA is often detected in soil, water, organisms, and even in human blood and breast milk. Hence, it is accessible to developing fetuses and nursing offspring after maternal exposure. The reported evidence for the endocrine disruption of TBBPA in the brain has raised concerns regarding its effects on neurodevelopmental and behavioral functions. This study investigated the effects of TBBPA exposure on neurodevelopment. A cell-based developmental neurotoxicity assay was performed to determine whether TBBPA is a developmental neurotoxicant. The assay revealed TBBPA to be a developmental neurotoxicant. C57BL/6N maternal mice were administered TBBPA at 0, 0.24, and 2.4 mg/kg during pregnancy and lactation, and their offspring underwent behavioral testing. The behavioral experiments revealed sex-specific effects. In females, only a deterioration of the motor ability was observed. In contrast, deteriorations in motor function, memory, and social interaction were noted in males. Furthermore, we validated changes in the expression of genes associated with behavioral abnormalities, confirming that perinatal exposure to TBBPA, at the administered doses, can affect neurodevelopment and behavior in offspring. These findings highlight the need for more in-depth and multifaceted research on the toxicity of TBBPA.
Keywords: Tetrabromobisphenol A; behavioral disorders; developmental neurotoxicity; endocrine disrupting chemicals; neurodevelopment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Maternal probiotic supplementation protects against PBDE-induced developmental, behavior and metabolic reprogramming in a sexually dimorphic manner: Role of gut microbiome.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jan;99(1):423-446. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03882-4. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39520540 Free PMC article.
-
NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Prenatal Development Studies of 2-((1-(4-Phenoxyphenoxy)propan-2-yl)oxy)pyridine (CASRN 95737-68-1) in Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley® SD®) Rats and New Zealand White (Hra:NZW SPF) Rabbits: DART Report 07 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. PMID: 35593777 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Olfactory toxicity of tetrabromobisphenol A to the goldfish Carassius auratus.J Hazard Mater. 2024 Nov 5;479:135661. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.135661. Epub 2024 Aug 27. J Hazard Mater. 2024. PMID: 39213767
-
Effects of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) on the reproductive health of male rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Aug 10;781:146745. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146745. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33794456
References
-
- Morose G. An Overview of Alternatives to Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) and Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) Lowell Center for Sustainable Production, University of Massachusetts; Lowell, MA, USA: 2006. [(accessed on 24 July 2025)]. Available online: https://www.uml.edu/docs/An%20Overview%20of%20Alternatives%20to%20Tetrab....
-
- IARC . Some Industrial Chemicals: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 115 International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2018.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

