HGF Overexpression in Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Cell Sheets Enhances Autophagy-Dependent Cytoprotection and Proliferation to Guard the Epicardial Mesothelium
- PMID: 40806435
- PMCID: PMC12347724
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157298
HGF Overexpression in Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Cell Sheets Enhances Autophagy-Dependent Cytoprotection and Proliferation to Guard the Epicardial Mesothelium
Abstract
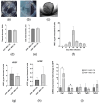
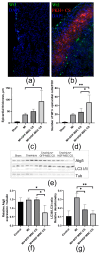
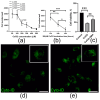
Epicardial mesothelial cells (EMCs), which form the epicardium, play a crucial role in cardiac homeostasis and repair. Upon damage, EMCs reactivate embryonic development programs, contributing to wound healing, progenitor cell amplification, and regulation of lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis, and fibrosis. However, the mechanisms governing EMC activation and subsequent regulation remain poorly understood. We hypothesized that hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a pleiotropic regulator of various cellular functions, could modulate EMC activity. To verify this hypothesis, we developed HGF-overexpressing mesenchymal stromal cell sheets (HGF-MSC CSs) and evaluated their effects on EMCs in vitro and in vivo. This study has revealed, for the first time, that EMCs express the c-Met (HGF receptor) on their surface and that both recombinant HGF and HGF-MSC CSs secretome cause c-Met phosphorylation, triggering downstream intracellular signaling. Our findings demonstrate that the HGF-MSC CSs secretome promotes cell survival under hypoxic conditions by modulating the level of autophagy. At the same time, HGF-MSC CSs stimulate EMC proliferation, promoting their amplification in the damage zone. These data demonstrate that HGF-MSC CSs can be considered a promising regulator of epicardial cell activity involved in heart repair after ischemic damage.
Keywords: HGF; cell sheets; epicardial cells; myocardial infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor facilitates the repair of spinal cord injuries by driving the chemotactic migration of mesenchymal stem cells through the β-catenin/TCF4/Nedd9 signaling pathway.Stem Cells. 2024 Nov 5;42(11):957-975. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxae055. Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 39269318
-
Mesenchymal stem cell secretome alters gene expression and upregulates motility of human endometrial stromal cells.Reproduction. 2023 Jul 5;166(2):161-174. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0485. Print 2023 Aug 1. Reproduction. 2023. PMID: 37252830 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
From signaling pathways to clinical trials: mesenchymal stem cells as multimodal regenerative architects in liver cirrhosis therapy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Aug 5;16(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04535-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40764597 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kumar Singh A., Kumar Jat R. Myocardial Infarction. Himal. J. Health Sci. 2022;6:16–32. doi: 10.22270/hjhs.v6i4.116. - DOI
-
- Al-Botaty B., El-Khoely A., Elsayed E.M., Eissa A.A. Insight into the Pathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction. Adv. Pharm. Res. 2022;6:223–237. doi: 10.21608/aprh.2022.155725.1188. - DOI
-
- Dergilev K.V., Komova A.V., Tsokolaeva Z.I., Beloglazova I.B., Parfyonova Y.V. Epicardium as a New Target for Regenerative Technologies in Cardiology. Genes Cells. 2020;15:33–40. doi: 10.23868/202004016. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

