Food-Derived Phytochemicals: Multicultural Approaches to Oxidative Stress and Immune Response
- PMID: 40806447
- PMCID: PMC12347654
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157316
Food-Derived Phytochemicals: Multicultural Approaches to Oxidative Stress and Immune Response
Abstract
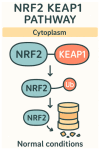
This review will focus on how ethnic consumption of foods such as shiitake, ginseng, turmeric, black seeds, berries, rosemary, moringa and holy basil can help act as antioxidants and immune modulators in fighting many diseases. We will investigate how these foods act on pathways like Nrf2/Keap1 to increase endogenous antioxidant capacity and help in reducing ROS production, based on publications found in PubMed between 1994 and 2024. In addition, we will show how these plants can cause immune system shifts by changing the makeup of the ratio of Th1/Th2 cells, reduce inflammation, and have antiangiogenic effects on cancer. This review will also show how plants can alter the gut microbiota and lead to a further decrease in oxidative stress. Overall, it will show how plants and their metabolites can potentially create a path forward for creating novel therapeutic approaches and help lead to an improved redox balance, support immune function, and enhance long-term health outcomes.
Keywords: Nrf2/Keap1 pathway; Th1/Th2 ratio; antioxidant; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cooper G.M. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd ed. Sinauer Associates; Sunderland, MA, USA: 2000. The development and causes of cancer.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources