Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase (FBA) Gene Family in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives
- PMID: 40806478
- PMCID: PMC12347426
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157348
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase (FBA) Gene Family in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives
Abstract
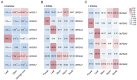
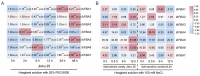
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA; EC 4.1.2.13) is a key enzyme in glycolysis and the Calvin cycle, which plays crucial roles in carbon allocation and plant growth. The FBA family genes (FBA s) have been identified in several plants. However, their presence and roles in sweet potato remain unexplored. In this study, a total of 20 FBAs were identified in sweet potato and its wild wild diploidrelatives, including seven in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas, 2n = 6x = 90), seven in I. trifida (2n = 2x = 30), and six in I. triloba (2n = 2x = 30). Their protein physicochemical properties, chromosomal localization, phylogenetic relationship, gene structure, promoter cis-elements, and expression patterns were systematically analyzed. The conserved genes and protein structures suggest a high degree of functional conservation among FBA genes. IbFBAs may participate in storage root development and starch biosynthesis, especially IbFBA1 and IbFBA6, which warrant further investigation as candidate genes. Additionally, the FBAs could respond to drought and salt stress. They are also implicated in hormone crosstalk, particularly with ABA and GA. This work provides valuable insights into the structure and function of FBAs and identifies candidate genes for improving yield, starch content, and abiotic stress tolerance in sweet potatoes.
Keywords: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase; Ipomoea trifida; Ipomoea triloba; abiotic stress; hormone crosstalk; starch biosynthesis; storage root development; sweet potato.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Li Q., Zhao H., Jin Y.L., Zhu J.C., Ma D.F. Analysis and perspectives of sweetpotato industry contributing to national food security in China. J. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022;38:1484–1491.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

