Unraveling the Translational Relevance of β-Hydroxybutyrate as an Intermediate Metabolite and Signaling Molecule
- PMID: 40806491
- PMCID: PMC12347605
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157362
Unraveling the Translational Relevance of β-Hydroxybutyrate as an Intermediate Metabolite and Signaling Molecule
Abstract
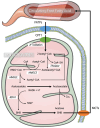
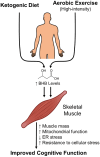
β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) is the most abundant ketone body produced during ketosis, a process initiated by glucose depletion and the β-oxidation of fatty acids in hepatocytes. Traditionally recognized as an alternative energy substrate during fasting, caloric restriction, and starvation, BHB has gained attention for its diverse signaling roles in various physiological processes. This review explores the emerging therapeutic potential of BHB in the context of sarcopenia, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. BHB influences gene expression, lipid metabolism, and inflammation through its inhibition of Class I Histone deacetylases (HDACs) and activation of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), specifically HCAR2 and FFAR3. These actions lead to enhanced mitochondrial function, reduced oxidative stress, and regulation of inflammatory pathways, with implication for muscle maintenance, neuroprotection, and metabolic regulation. Moreover, BHB's ability to modulate adipose tissue lipolysis and immune responses highlight its broader potential in managing chronic metabolic conditions and aging. While these findings show BHB as a promising therapeutic agent, further research is required to determine optimal dosing strategies, long-term effects, and its translational potential in clinical settings. Understanding BHB's mechanisms will facilitate its development as a novel therapeutic strategy for multiple organ systems affected by aging and disease.
Keywords: inflammation; lipolysis; neurodegenerative diseases; sarcopenia; β-hydroxybutyrate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Multifaceted Influence of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate on Autophagy, Mitochondrial Metabolism, and Epigenetic Regulation.J Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun;126(6):e70050. doi: 10.1002/jcb.70050. J Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40583323 Review.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) elicits concentration-dependent anti-inflammatory effects on microglial cells which are reversible by blocking its monocarboxylate (MCT) importer.Front Aging. 2025 Jul 29;6:1628835. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1628835. eCollection 2025. Front Aging. 2025. PMID: 40800722 Free PMC article.
-
β-hydroxybutyrate, a ketone body, suppresses tumor growth, stemness, and invasive phenotypes in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2025 Dec;26(1):2516825. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2025.2516825. Epub 2025 Jun 22. Cancer Biol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40545696
-
Impact of fasting & ketogenic interventions on the NLRP3 inflammasome: A narrative review.Biomed J. 2024 Feb;47(1):100677. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.100677. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Biomed J. 2024. PMID: 37940045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ehtiati S., Hatami B., Khatami S.H., Tajernarenj K., Abdi S., Sirati-Sabet M., Hasemi S.A.H.G., Ahmadzade R., Hamed N., Goudarzi M., et al. The Multifaceted Influence of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate on Autophagy, Mitochondrial Metabolism, and Epigenetic Regulation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2025;126:e70050. doi: 10.1002/jcb.70050. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nesterova V.V., Babenkova P.I., Brezgunova A.A., Samoylova N.A., Sadovnikova I.S., Semenovich D.S., Andrianova N.V., Gureev A.P., Plotnikov E.Y. Differences in the Effect of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate on the Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Markers in Tissues from Young and Old Rats. Biochemistry. 2024;89:1336–1348. doi: 10.1134/S0006297924070149. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

