Investigating the Cellular Responses to Combined Nisin and Urolithin B Treatment (7:3) in HKB-11 Lymphoma Cells
- PMID: 40806497
- PMCID: PMC12347767
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157369
Investigating the Cellular Responses to Combined Nisin and Urolithin B Treatment (7:3) in HKB-11 Lymphoma Cells
Abstract
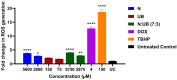
Lymphoma continues to pose a serious challenge to global health, underscoring the urgent need for new therapeutic strategies. Recently, the gut microbiome has been shown to play a potential role in regulating immune responses and influencing cancer progression. However, its molecular mechanisms of action in lymphoma remain poorly understood. This study investigates the antiproliferative and apoptotic activities of gut microbiota-derived metabolites, specifically nisin (N) and urolithin B (UB), individually and in combination 7:3 (5750 μM), against the human lymphoma cell line HKB-11. Comprehensive evaluations were performed using Alamar Blue viability assays, combination index (CI) analyses, reactive oxygen species (ROS) quantification, flow cytometry for apoptosis detection, and advanced bottom-up proteomics analyses. N and UB exhibited potent antiproliferative activity, with the 7:3 combination demonstrating strong synergistic effects (CI < 1), significantly enhancing apoptosis (p < 0.01) and ROS production (p < 0.0001) compared to the untreated control. Proteomics analyses revealed substantial alterations in proteins crucial to ribosomal biogenesis, mitochondrial function, cell cycle control, and apoptosis regulation, including a marked downregulation of ribosomal proteins (RPS27; Log2FC = -3.47) and UBE2N (Log2FC = -0.60). These findings highlight the potential of N and UB combinations as a novel and practical therapeutic approach for lymphoma treatment, warranting further in vivo exploration and clinical validation.
Keywords: apoptosis; lymphoma; nisin; postbiotics; proteomics; synergy; urolithin B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gut Microbial Postbiotics as Potential Therapeutics for Lymphoma: Proteomics Insights of the Synergistic Effects of Nisin and Urolithin B Against Human Lymphoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 16;26(14):6829. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146829. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725093 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation and comparison of the anti-proliferative and anti-metastatic effects of urolithin A and urolithin B against esophageal cancer cells: an in vitro and in silico study.Daru. 2025 Jul 31;33(2):28. doi: 10.1007/s40199-025-00570-1. Daru. 2025. PMID: 40742486
-
Erbium oxide nanoparticles induce potent cell death, genomic instability and ROS-mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated apoptosis in U937 lymphoma cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):11027-11039. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03962-x. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40072553 Free PMC article.
-
3-Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA) induced antiproliferative effect by suppressing Notch signaling pathway and synergistic interaction with cisplatin against prostate cancer cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):10379-10398. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03899-1. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39985578
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swerdlow S.H., Campo E., Pileri S.A., Harris N.L., Stein H., Siebert R., Advani R., Ghielmini M., Salles G.A., Zelenetz A.D. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2016;127:2375–2390. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J., Ervik M., Lam F., Colombet M., Mery L., Piñeros M., Znaor A., Soerjomataram I., Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2020. Cancer Tomorrow, 2021.
-
- Sadrekarimi H., Gardanova Z.R., Bakhshesh M., Ebrahimzadeh F., Yaseri A.F., Thangavelu L., Hasanpoor Z., Zadeh F.A., Kahrizi M.S. Emerging role of human microbiome in cancer development and response to therapy: Special focus on intestinal microflora. J. Transl. Med. 2022;20:301. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03492-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

