Sepsis Prediction: Biomarkers Combined in a Bayesian Approach
- PMID: 40806505
- PMCID: PMC12347722
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157379
Sepsis Prediction: Biomarkers Combined in a Bayesian Approach
Abstract
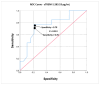
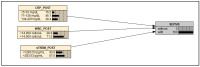
Sepsis is a serious public health problem. sTREM-1 is a marker of inflammatory and infectious processes that has the potential to become a useful tool for predicting the evolution of sepsis. A prediction model for sepsis was constructed by combining sTREM-1, CRP, and a leukogram via a Bayesian network. A translational study carried out with 32 children with congenital heart disease who had undergone surgical correction at a public referral hospital in Northeast Brazil. In the postoperative period, the mean value of sTREM-1 was greater among patients diagnosed with sepsis than among those not diagnosed with sepsis (394.58 pg/mL versus 239.93 pg/mL, p < 0.001). Analysis of the ROC curve for sTREM-1 and sepsis revealed that the area under the curve was 0.761, with a 95% CI (0.587-0.935) and p = 0.013. With the Bayesian model, we found that a 100% probability of sepsis was related to postoperative blood concentrations of CRP above 71 mg/dL, a leukogram above 14,000 cells/μL, and sTREM-1 concentrations above the cutoff point (283.53 pg/mL). The proposed model using the Bayesian network approach with the combination of CRP, leukocyte count, and postoperative sTREM-1 showed promise for the diagnosis of sepsis.
Keywords: Bayes theorem; biomarkers; cardiac surgery; sTREM-1; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Clinical study on the effect of glycosaminoglycans on vascular endothelial glycocalyx in sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Jun;37(6):527-534. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240725-00634. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40820527 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Assessment of S100A8/A9 and resistin as predictive biomarkers for mortality in critically ill patients with sepsis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 3;15:1555307. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1555307. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40568710 Free PMC article.
-
Role of sTREM-1 in predicting mortality of infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2016 May 13;6(5):e010314. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010314. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27178971 Free PMC article.
-
Human neutrophil lipocalin, procalcitonin, c-reactive protein, and leucocyte count for prediction of bacterial sepsis in emergency department patients.Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2025 Jul 1;33(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13049-025-01429-9. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40598497 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of plasma sTREM-1 for sepsis diagnosis in systemic inflammatory patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2012 Nov 29;16(6):R229. doi: 10.1186/cc11884. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 23194114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Latin American Sepsis Institute Care for Pediatric Patients with Sepsis, Severe Sepsis, and Septic Shock. 2019. [(accessed on 10 July 2025)]. Available online: https://ilas.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/protocolo-de-tratamento-p....
-
- de Souza D.C., Gonçalves Martin J., Soares Lanziotti V., de Oliveira C.F., Tonial C., de Carvalho W.B., Roberto Fioretto J., Pedro Piva J., Juan Troster E., Siqueira Bossa A., et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in paediatric intensive care units in Brazil (the Sepsis PREvalence Assessment Database in Pediatric population, SPREAD PED): An observational study. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health. 2021;5:873–881. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00286-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Souza D.C., Barreira E.R., Shieh H.H., Ventura A.M.C., Bousso A., Troster E.J. Prevalence and outcomes of sepsis in children hospitalized in public and private hospitals in Latin America: A multicenter observational study. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiva. 2021;33:231–242. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20210030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

