Isorhamnetin: Reviewing Recent Developments in Anticancer Mechanisms and Nanoformulation-Driven Delivery
- PMID: 40806510
- PMCID: PMC12347436
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157381
Isorhamnetin: Reviewing Recent Developments in Anticancer Mechanisms and Nanoformulation-Driven Delivery
Abstract
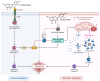
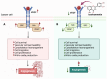
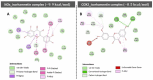
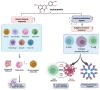
Natural compounds, particularly flavonoids, have emerged as promising anticancer agents due to their various biological activities and no or negligible toxicity towards healthy tissues. Among these, isorhamnetin, a methylated flavonoid, has gained significant attention for its potential to target multiple cancer hallmarks. This review comprehensively explores the mechanisms by which isorhamnetin exerts its anticancer effects, including cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, suppression of metastasis and angiogenesis, and modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Notably, isorhamnetin arrests cancer cell proliferation by regulating cyclins, and CDKs induce apoptosis via caspase activation and mitochondrial dysfunction. It inhibits metastatic progression by downregulating MMPs, VEGF, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers. Furthermore, its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties mitigate reactive oxygen species (ROS) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, restricting cancer progression and modulating tumor microenvironments. Combining isorhamnetin with other treatments was also discussed to overcome multidrug resistance. Importantly, this review integrates the recent literature (2022-2024) and highlights isorhamnetin's roles in modulating cancer-specific signaling pathways, immune evasion, tumor microenvironment dynamics, and combination therapies. We also discuss nanoformulation-based strategies that significantly enhance isorhamnetin's delivery and bioavailability. This positions isorhamnetin as a promising adjunct in modern oncology, capable of improving therapeutic outcomes when used alone or in synergy with conventional treatments. The future perspectives and potential research directions were also summarized. By consolidating current knowledge and identifying critical research gaps, this review positions Isorhamnetin as a potent and versatile candidate in modern oncology, offering a pathway toward safer and more effective cancer treatment strategies.
Keywords: anticancer; apoptosis; isorhamnetin flavonoids; metastasis; nanoformulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Oleocanthal as a Multifunctional Anti-Cancer Agent: Mechanistic Insights, Advanced Delivery Strategies, and Synergies for Precision Oncology.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 9;26(12):5521. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125521. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol in oral cancer: a systematic review of preclinical studies on its anticancer mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 13;42(8):329. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02903-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40653555
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

