Quercetin as an Anti-Diabetic Agent in Rodents-Is It Worth Testing in Humans?
- PMID: 40806520
- PMCID: PMC12347388
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157391
Quercetin as an Anti-Diabetic Agent in Rodents-Is It Worth Testing in Humans?
Abstract
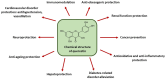
Quercetin is a biologically active flavonoid compound that exerts numerous beneficial effects in humans and animals, including anti-diabetic activity. Its action has been explored in rodent models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It was revealed that quercetin mitigated diabetes-related hormonal and metabolic disorders and reduced oxidative and inflammatory stress. Its anti-diabetic effects were associated with advantageous changes in the relevant enzymes and signaling molecules. Quercetin positively affected, among others, superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glucose transporter-2, glucokinase, glucose-6-phosphatase, glycogen phosphorylase, glycogen synthase, glycogen synthase kinase-3β, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, silent information regulator-1, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1, insulin receptor substrate 1, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and protein kinase B. The available data support the conclusion that the action of quercetin was pleiotropic since it alleviates a wide range of diabetes-related disorders. Moreover, no side effects were observed during treatment with quercetin in rodents. Given that human diabetes affects a large part of the population worldwide, the results of animal studies encourage clinical trials to evaluate the potential of quercetin as an adjunct to pharmacological therapies.
Keywords: diabetes; metabolism; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Pharmacological treatment of children with gastro-oesophageal reflux.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 24;2014(11):CD008550. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008550.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 22;8:CD008550. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008550.pub3. PMID: 25419906 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Phosphorylase Kinase Deficiency.2011 May 31 [updated 2018 Nov 1]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2011 May 31 [updated 2018 Nov 1]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 21634085 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials