The Characterization of the Neuroimmune Response in Primary Pterygia
- PMID: 40806545
- PMCID: PMC12346938
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157417
The Characterization of the Neuroimmune Response in Primary Pterygia
Abstract
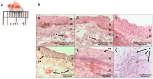
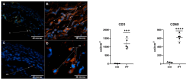
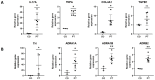
Several chronic inflammatory processes are currently being studied in relation to other systems to better understand the regulation mechanisms and identify potential therapeutic targets. A significant body of evidence supports the role of the nervous system in regulating various immunological processes. This study investigates the relationship between pterygia and the sympathetic nervous system, focusing on their interaction in the inflammatory response and fibrogenic process. Sixteen surgical specimens of primary pterygia and four conjunctival tissue samples were examined, and their morphology was analyzed using hematoxylin-eosin and Masson's trichrome stains. The gene expression of adrenergic receptors, as well as inflammatory and fibrogenic cytokines, was also assessed. Additionally, both adrenergic receptors and tyrosine hydroxylase were found to be localized within the tissues according to immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence techniques. Increased expression of proinflammatory, fibrogenic, and adrenergic genes was observed in the pterygium compared to the healthy conjunctiva. Adrenergic receptors and tyrosine hydroxylase were localized in the basal region of the epithelium and within blood vessels, closely associated with immune cells. Neuroimmunomodulation plays a key role in the pathogenesis of pterygia by activating the sympathetic nervous system. At the intravascular level, norepinephrine promotes the migration of immune cells, thereby sustaining inflammation. Additionally, sympathetic nerve fibers located at the subepithelial level contribute to epithelial growth and the fibrosis associated with pterygia.
Keywords: fibrogenic; inflammation; neuroimmune; pterygium; response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Conjunctival autograft for pterygium.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Feb 11;2(2):CD011349. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011349.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26867004 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Expression and the pro-fibrotic effects of Mesenchyme homeobox 1 in patients with pterygium.Exp Eye Res. 2025 Sep;258:110479. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2025.110479. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Exp Eye Res. 2025. PMID: 40482762
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Domdey M., Kluth M.A., Maßlo C., Ganss C., Frank M.H., Frank N.Y., Coroneo M., Cursiefen C., Notara M. Consecutive dosing of UVB irradiation induces loss of ABCB5 expression and activation of EMT and fibrosis proteins in limbal epithelial cells similar to pterygium epithelium. Stem. Cell Res. 2022;64:102936. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2022.102936. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

