Elevated IGFBP4 and Cognitive Impairment in a PTFE-Induced Mouse Model of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- PMID: 40806552
- PMCID: PMC12348007
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157423
Elevated IGFBP4 and Cognitive Impairment in a PTFE-Induced Mouse Model of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
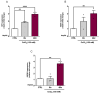
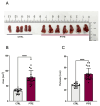
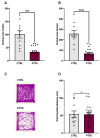
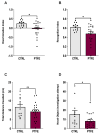
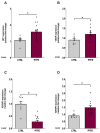
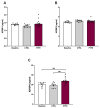
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a prevalent disorder linked to metabolic complications such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. By fragmenting normal sleep architecture, OSA perturbs the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor (GH/IGF) axis and alters circulating levels of IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs). A prior clinical observation of elevated IGFBP4 in OSA patients motivated the present investigation in a controlled animal model. Building on the previously reported protocol, OSA was induced in male C57BL/6 mice (9-12 weeks old) through intralingual injection of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), producing tongue hypertrophy, intermittent airway obstruction, and hypoxemia. After 8-10 weeks, the study assessed (1) hypoxia biomarkers-including HIF-1α and VEGF expression-and (2) neurobehavioral outcomes in anxiety and cognition using the open-field and novel object recognition tests. PTFE-treated mice exhibited a significant increase in circulating IGFBP4 versus both baseline and control groups. Hepatic Igfbp4 mRNA was also upregulated. Behaviorally, PTFE mice displayed heightened anxiety-like behavior and impaired novel object recognition, paralleling cognitive deficits reported in human OSA. These findings validate the PTFE-induced model as a tool for studying OSA-related hypoxia and neurocognitive dysfunction, and they underscore IGFBP4 as a promising biomarker and potential mediator of OSA's systemic effects.
Keywords: IGFBP4; OSA animal model; biomarker; hypoxia; novel object recognition; obstructive sleep apnea; open field test.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

