Multiplex Immunofluorescence Reveals Therapeutic Targets EGFR, EpCAM, Tissue Factor, and TROP2 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 40806559
- PMCID: PMC12347865
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157430
Multiplex Immunofluorescence Reveals Therapeutic Targets EGFR, EpCAM, Tissue Factor, and TROP2 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
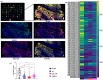
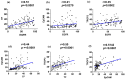
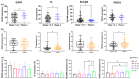
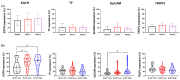
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a clinically and molecularly heterogeneous subtype defined by the absence of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) expression. In this study, tumor specimens from 104 TNBC patients were analyzed to characterize molecular and clinicopathological features and to assess the expression and therapeutic potential of four key surface markers: epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), tissue factor (TF), and trophoblast cell surface antigen (TROP2). Multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) demonstrated elevated EGFR and TROP2 expression in the majority of samples. Significant positive correlations were observed between EGFR and TF, as well as between TROP2 and both TF and EpCAM. Expression analyses revealed increased EGFR and TF levels with advancing tumor stage, whereas EpCAM expression declined in advanced-stage tumors. TROP2 and TF expression were significantly elevated in higher-grade tumors. Additionally, EGFR and EpCAM levels were significantly higher in patients with elevated Ki-67 indices. Binding specificity assays using single-chain variable fragment (scFv-SNAP) fusion proteins confirmed robust targeting efficacy, particularly for EGFR and TROP2. These findings underscore the therapeutic relevance of EGFR and TROP2 as potential biomarkers and targets in TNBC.
Keywords: EGFR; EpCAM; TROP2; multiplex immunofluorescence; tissue factor; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative Multiplex Immunofluorescence Assay for Trophoblast Cell-Surface Antigen 2 and Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Expression in Breast Cancer: Toward Guiding Patient Selection for Antibody-Drug Conjugate Therapies.JCO Precis Oncol. 2025 Jul;9:e2500128. doi: 10.1200/PO-25-00128. Epub 2025 Jul 16. JCO Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40669019
-
[99mTc]Tc-MY6349 Probe for Trop2-Targeted SPECT Imaging: From Preclinical to Pilot Clinical Study.J Nucl Med. 2025 Apr 1;66(4):543-551. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.268564. J Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 39947911 Clinical Trial.
-
Expression patterns of TROP2 and Nectin-4 in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in relation to HPV status: potential biomarkers for targeted therapy.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025 Aug 18;17:17588359251361877. doi: 10.1177/17588359251361877. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40838147 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted therapy approaches for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in triple negative breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 10;14:1431418. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1431418. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39450256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptor-defined subtypes of breast cancer in indigenous populations in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Med. 2014 Sep 9;11(9):e1001720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001720. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Med. 2014. PMID: 25202974 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

