From Hypoxia to Bone: Reprogramming the Prostate Cancer Metastatic Cascade
- PMID: 40806577
- PMCID: PMC12347711
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157452
From Hypoxia to Bone: Reprogramming the Prostate Cancer Metastatic Cascade
Abstract
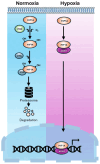
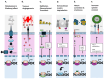
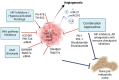
Bone is the most frequent site of distant metastasis in advanced prostate cancer (PCa), contributing substantially to patient morbidity and mortality. Hypoxia, a defining feature of the solid tumour microenvironment, plays a pivotal role in driving bone-tropic progression by promoting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), cancer stemness, extracellular matrix (ECM) remodelling, and activation of key signalling pathways such as Wingless/Integrated (Wnt) Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/Akt. Hypoxia also enhances the secretion of extracellular vesicles (EVs), enriched with pro-metastatic cargos, and upregulates bone-homing molecules including CXCR4, integrins, and PIM kinases, fostering pre-metastatic niche formation and skeletal colonisation. In this review, we analysed current evidence on how hypoxia orchestrates PCa dissemination to bone, focusing on the molecular crosstalk between HIF signalling, Wnt activation, EV-mediated communication, and cellular plasticity. We further explore therapeutic strategies targeting hypoxia-related pathways, such as HIF inhibitors, hypoxia-activated prodrugs, and Wnt antagonists, with an emphasis on overcoming therapy resistance in castration-resistant PCa (CRPC). By examining the mechanistic underpinnings of hypoxia-driven bone metastasis, we highlight promising translational avenues for improving patient outcomes in advanced PCa.
Keywords: EMT; HIF-1α; Wnt signalling; bone metastasis; extracellular vesicles; hypoxia; prostate cancer; therapy resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration-resistant prostate cancer.Eur Urol. 2014 Feb;65(2):467-79. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Eur Urol. 2014. PMID: 24321502
-
Intercellular communication between extracellular vesicles from conditioned macrophages and breast cancer cells drives endocrine therapy resistance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 3;13:1548724. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1548724. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40567500 Free PMC article.
-
CAF-mediated regulation of prostate cancer stem cell stemness via the Wnt/β-catenin and SDF-1/CXCR4 pathways in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 15;13:1617200. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1617200. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40735647 Free PMC article.
-
Sending the Signal to Bone: How Tumor-Derived EVs Orchestrate Pre-Metastatic Niche Formation and Skeletal Colonization.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 4;13(7):1640. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071640. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and characterization of bone mesenchymal cell small extracellular vesicles using a novel mouse model.J Bone Miner Res. 2024 Oct 29;39(11):1633-1643. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjae135. J Bone Miner Res. 2024. PMID: 39173022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poon D.M.C., Cheung W.S.K., Chiu P.K.F., Chung D.H.S., Kung J.B.T., Lam D.C.M., Leung A.K.C., Ng A.C.F., O’Sullivan J.M., Teoh J.Y.C., et al. Treatment of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Review of Current Evidence and Synthesis of Expert Opinions on Radioligand Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2025;15:1530580. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1530580. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kfoury Y., Baryawno N., Severe N., Mei S., Gustafsson K., Hirz T., Brouse T., Scadden E.W., Igolkina A.A., Kokkaliaris K., et al. Human Prostate Cancer Bone Metastases Have an Actionable Immunosuppressive Microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2021;39:1464–1478.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.09.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

