Polymorphic Variants of Selected Genes Regulating Bile Acid Homeostasis in Women with Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy
- PMID: 40806580
- PMCID: PMC12347146
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157456
Polymorphic Variants of Selected Genes Regulating Bile Acid Homeostasis in Women with Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy
Abstract
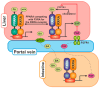
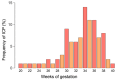
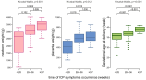
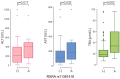
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) is characterized by the onset of pruritus and elevated serum transaminases and bile acids (BA). The key enzyme in BA synthesis is CYP7A1, and its functions are regulated by various nuclear receptors. The goal of this study is to evaluate the association between CYP7A1, NR1H1, RXRA, and PPARA gene variants and risk of ICP. Five single nucleotide variants (SNVs), rs3808607 (CYP7A1), rs56163822 (NR1H4), rs1800206 (PPARA), rs749759, and rs11381416 (NR2B1), were genotyped in a group of 96 ICP and 211 controls. The T allele of the CYP7A1 (rs3808607) variant may be a protective factor against ICP risk (OR = 0.697, 95% CI: 0.495-0.981, p = 0.038). Genetic model analysis showed that rs3808607 was associated with decreased risk of ICP under dominant (OR = 0.55, 95% CI: 0.32-3.16, p = 0.032, AIC = 380.9) and log-additive models (OR = 0.71, 95% CI: 0.51-1.00, p = 0.046, AIC = 381.4). The A insertion in the rs11381416 NR2B1 variant was associated with the degree of elevation in the liver function tests TBA (34.3 vs. 18.8 μmol/L, p = 0.002), ALT (397.0 vs. 213.0 IU/L, p = 0.017), and AST (186.0 vs. 114.4 IU/L, p = 0.032) in ICP women. Results indicate an association between the CYP7A1 rs3808607 and the risk of ICP and the association of the rs11381416 of the NR2B1 receptor with higher values of liver function tests in women with ICP. A better understanding of the cooperation of proteins involved in BA metabolism may have important therapeutic implications in ICP and other hepatobiliary diseases.
Keywords: genes regulating bile acid homeostasis; intrahepatic cholestasis; polymorphic variants; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between ABCB4 variants and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 26;15(1):3300. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87909-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39865141 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
Distinct response to treatment and characteristics of bile acid composition of early- and late-onset intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: A prospective pilot study.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025 Jul 2. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.70247. Online ahead of print. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 40600592
-
Whole-exome sequencing identifies novel mutation in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: A case report and literature review.Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 2025 Aug;229(4):288-293. doi: 10.1055/a-2468-5250. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 2025. PMID: 39814052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Atypical Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome.2007 Nov 16 [updated 2021 Sep 23]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2007 Nov 16 [updated 2021 Sep 23]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301541 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

