Opioid Use in Cancer Pain Management: Navigating the Line Between Relief and Addiction
- PMID: 40806585
- PMCID: PMC12347026
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157459
Opioid Use in Cancer Pain Management: Navigating the Line Between Relief and Addiction
Abstract
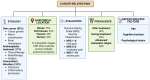
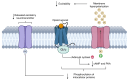
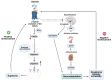
The use of opioids for cancer-related pain is essential but poses significant challenges due to the risk of misuse and the development of opioid use disorder (OUD). This review takes a multidisciplinary perspective based on the current scientific literature to analyze the pharmacological mechanisms, classification, and therapeutic roles of opioids in oncology. Key risk factors for opioid misuse-including psychiatric comorbidities, prior substance use, and insufficient clinical monitoring-are discussed in conjunction with validated tools for pain assessment and international guidelines. The review emphasizes the importance of integrating toxicological, pharmacological, physiological, and public health perspectives to promote rational opioid use. Pharmacogenetic variability is explored as a determinant of treatment response and addiction risk, underscoring the value of personalized medicine. Evidence-based strategies such as early screening, psychosocial interventions, and the use of buprenorphine-naloxone are presented as effective measures for managing OUD in cancer patients. Ultimately, this work advocates for safe, patient-centered opioid prescribing practices that ensure effective pain relief without compromising safety or quality of life.
Keywords: addiction prevention; cancer-related pain; opioid use disorder; opioids; pain management; personalized medicine; pharmacogenetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feitelson M.A., Arzumanyan A., Kulathinal R.J., Blain S.W., Holcombe R.F., Mahajna J., Marino M., Martinez-Chantar M.L., Nawroth R., Sanchez-Garcia I., et al. Sustained proliferation in cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015;35:S25–S54. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

