Metabolic Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: Implications for Targeted Therapy
- PMID: 40806636
- PMCID: PMC12346973
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157508
Metabolic Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: Implications for Targeted Therapy
Abstract
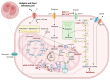
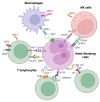
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is a biologically and clinically unique malignancy characterized by rare Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells surrounded by a dense and diverse inflammatory infiltrate. These malignant cells actively reshape the tumor microenvironment (TME) through metabolic reprogramming and immune evasion strategies. This review synthesizes current knowledge on how metabolic alterations contribute to tumor survival, immune dysfunction, and therapeutic resistance in cHL. We discuss novel therapeutic approaches aimed at disrupting these processes and examine the potential of combining metabolic interventions with immune-based strategies-such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs), epigenetic modulators, bispecific antibodies, and CAR-T/CAR-NK cell therapies-which may help overcome resistance and enhance anti-tumor responses. Several agents are currently under investigation for their ability to modulate immune cell metabolism and restore effective immune surveillance. Altogether, targeting metabolic vulnerabilities within both tumor and immune compartments offers a promising, multifaceted strategy to improve clinical outcomes in patients with relapsed or refractory cHL.
Keywords: Hodgkin lymphoma; cell metabolism; therapeutic strategies; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Immunotherapy and Immune Modulators in Hormone-Positive Breast Cancer: Implications for Localized and Metastatic Disease.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 17;14(12):4322. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124322. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40566067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between tumor mutation burden and the tumor microenvironment predicts the prognosis of pan-cancer anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1557461. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557461. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40777041 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal P., Limaiem F. Brenner’s Encyclopedia of Genetics. 2nd ed. Elsevier Science; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2025. Reed-Sternberg Cells; pp. 113–115. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

