Antioxidants and Reactive Oxygen Species: Shaping Human Health and Disease Outcomes
- PMID: 40806653
- PMCID: PMC12347716
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157520
Antioxidants and Reactive Oxygen Species: Shaping Human Health and Disease Outcomes
Abstract
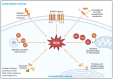
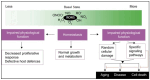
Reactive molecules, including oxygen and nitrogen species, serve dual roles in human physiology. While they function as essential signaling molecules under normal physiological conditions, they contribute to cellular dysfunction and damage when produced in excess by normal metabolism or in response to stressors. Oxidative/nitrosative stress is a pathological state, resulting from the overproduction of reactive species exceeding the antioxidant capacity of the body, which is implicated in several chronic human diseases. Antioxidant therapies aimed at restoring redox balance and preventing oxidative/nitrosative stress have demonstrated efficacy in preclinical models. However, their clinical applications have met with inconsistent success owing to efficacy, safety, and bioavailability concerns. This summative review analyzes the role of reactive species in human pathophysiology, the mechanisms of action of antioxidant protection, and the challenges that hinder their translation into effective clinical therapies in order to evaluate potential emerging strategies such as targeted delivery systems, precision medicine, and synergistic therapeutic approaches, among others, to overcome current limitations. By integrating recent advances, this review highlights the value of targeting reactive species in the prevention and management of chronic diseases.
Keywords: chronic diseases; inflammation; nanomedicine; nitrosative stress; oxidation; oxidative stress; precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest declared by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Pham T.-P.-T., Le T.-H.-T., Pham H.-T.-X., Tran T.-T., Pham V.-T., Mafruhah O.R., Ha H.-A. Comparative efficacy of antioxidant therapies for sepsis and septic shock in the intensive care unit: A frequentist network meta-analysis. Heliyon. 2024;10:e31447. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31447. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smith C.J., Perfetti T.A., King J.A. Indirect oxidative stress from pulmonary inflammation exceeds direct oxidative stress from chemical damage to mitochondria. Toxicol. Res. Appl. 2019;3:2397847319842845. doi: 10.1177/2397847319842845. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

