Deciphering the Role of Functional Ion Channels in Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) and Their Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 40806720
- PMCID: PMC12347136
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157595
Deciphering the Role of Functional Ion Channels in Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) and Their Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
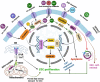
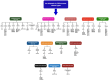
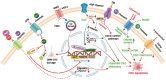
Despite advances in medicine, cancer remains one of the foremost global health concerns. Conventional treatments like surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy have advanced with the emergence of targeted and immunotherapy approaches. However, therapeutic resistance and relapse remain major barriers to long-term success in cancer treatment, often driven by cancer stem cells (CSCs). These rare, resilient cells can survive therapy and drive tumour regrowth, urging deeper investigation into the mechanisms underlying their persistence. CSCs express ion channels typical of excitable tissues, which, beyond electrophysiology, critically regulate CSC fate. However, the underlying regulatory mechanisms of these channels in CSCs remain largely unexplored and poorly understood. Nevertheless, the therapeutic potential of targeting CSC ion channels is immense, as it offers a powerful strategy to disrupt vital signalling pathways involved in numerous pathological conditions. In this review, we explore the diverse repertoire of ion channels expressed in CSCs and highlight recent mechanistic insights into how these channels modulate CSC behaviours, dynamics, and functions. We present a concise overview of ion channel-mediated CSC regulation, emphasizing their potential as novel diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets, and identifying key areas for future research.
Keywords: cancer stem cell; cancer therapeutics; cellular signalling; ion channel-targeted therapy; ion channels; tumour microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
An update on cancer stem cell survival pathways involved in chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer.Future Oncol. 2025 Mar;21(6):715-735. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2461443. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39936282 Review.
-
Cancer stem cells: advances in knowledge and implications for cancer therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jul 5;9(1):170. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01851-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38965243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer stem cells: mitochondria signalling pathway and strategies for therapeutic interventions.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 3;52(1):671. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10748-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40608151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cervical cancer stem cells: opportunities and challenges.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Nov;141(11):1889-97. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1905-y. Epub 2015 Jan 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25563493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical