AMPK-Targeting Effects of (-)-Epicatechin Gallate from Hibiscus sabdariffa Linne Leaves on Dual Modulation of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Glycogen Synthesis in an In Vitro Oleic Acid Model
- PMID: 40806739
- PMCID: PMC12347588
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157612
AMPK-Targeting Effects of (-)-Epicatechin Gallate from Hibiscus sabdariffa Linne Leaves on Dual Modulation of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Glycogen Synthesis in an In Vitro Oleic Acid Model
Abstract
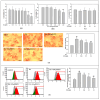
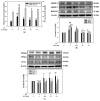
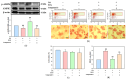
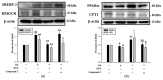
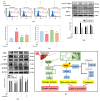
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) begins with hepatic lipid accumulation and triggers insulin resistance. Hibiscus leaf extract exhibits antioxidant and anti-atherosclerotic activities, and is rich in (-)-epicatechin gallate (ECG). Despite ECG's well-known pharmacological activities and its total antioxidant capacity being stronger than that of other catechins, its regulatory effects on MASLD have not been fully described previously. Therefore, this study attempted to evaluate the anti-MASLD potential of ECG isolated from Hibiscus leaves on abnormal lipid and glucose metabolism in hepatocytes. First, oleic acid (OA) was used as an experimental model to induce lipid dysmetabolism in human primary hepatocytes. Treatment with ECG can significantly (p < 0.05) reduce the OA-induced cellular lipid accumulation. Nile red staining revealed, compared to the OA group, the inhibition percentages of 29, 61, and 82% at the tested doses of ECG, respectively. The beneficial effects of ECG were associated with the downregulation of SREBPs/HMGCR and upregulation of PPARα/CPT1 through targeting AMPK. Also, ECG at 0.4 µM produced a significant (p < 0.01) decrease in oxidative stress by 83%, and a marked (p < 0.05) increase in glycogen synthesis by 145% on the OA-exposed hepatocytes with insulin signaling blockade. Mechanistic assays indicated lipid and glucose metabolic homeostasis of ECG might be mediated via regulation of lipogenesis, fatty acid β-oxidation, and insulin resistance, as confirmed by an AMPK inhibitor. These results suggest ECG is a dual modulator of lipid and carbohydrate dysmetabolism in hepatocytes.
Keywords: (−)-epicatechin gallate; AMPK; Hibiscus leaves; glycogen synthesis; insulin resistance; lipid accumulation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Herbal mixture of Platycodon grandiflorum, Cinnamomum cassia, and Asiasarum sieboldii extracts protects against NASH progression via regulation of hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and apoptosis.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:157077. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157077. Epub 2025 Jul 14. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40684491
-
Alleviation of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease by silymarin is associated with maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis via regulation of optic atrophy 1.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2025 Jul;392(7):103611. doi: 10.1016/j.jpet.2025.103611. Epub 2025 May 19. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2025. PMID: 40505414
-
Elucidating the mechanistic interplay of AMPK and Nrf2 in MASLD: A focus on dietary phytochemical modulation of lipid and redox homeostasis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Sep 1;777:152300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.152300. Epub 2025 Jul 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40633499 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rinella M.E., Lazarus J.V., Ratziu V., Francque S.M., Sanyal A.J., Kanwal F., Romero D., Abdelmalek M.F., Anstee Q.M., Arab J.P., et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology. 2023;78:1966–1986. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000520. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

