Navigating the Landscape of Liquid Biopsy in Colorectal Cancer: Current Insights and Future Directions
- PMID: 40806747
- PMCID: PMC12347742
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157619
Navigating the Landscape of Liquid Biopsy in Colorectal Cancer: Current Insights and Future Directions
Abstract
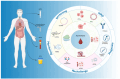
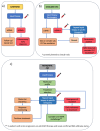
Liquid biopsy has emerged as a valuable tool for the detection and monitoring of colorectal cancer (CRC), providing minimally invasive insights into tumor biology through circulating biomarkers such as circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), circulating tumor cells (CTCs), microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs). Additional biomarkers, including tumor-educated platelets (TEPs) and exosomal RNAs, offer further potential for early detection and prognostic role, although ongoing clinical validation is still needed. This review summarizes the current evidence on the diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive capabilities of liquid biopsy in both metastatic and non-metastatic CRC. In the non-metastatic setting, liquid biopsy is gaining traction in early detection through screening and in identifying minimal residual disease (MRD), potentially guiding adjuvant treatment and reducing overtreatment. In contrast, liquid biopsy is more established in metastatic CRC for monitoring treatment responses, clonal evolution, and mechanisms of resistance. The integration of ctDNA-guided treatment algorithms into clinical practice could optimize therapeutic strategies and minimize unnecessary interventions. Despite promising advances, challenges remain in assay standardization, early-stage sensitivity, and the integration of multi-omic data for comprehensive tumor profiling. Future efforts should focus on enhancing the sensitivity of liquid biopsy platforms, validating emerging biomarkers, and expanding multi-omic approaches to support more targeted and personalized treatment strategies across CRC stages.
Keywords: adjuvant therapy guidance; colorectal cancer; liquid biopsy; minimal residual disease; resistance mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advancements in liquid biopsy for breast Cancer: Molecular biomarkers and clinical applications.Cancer Treat Rev. 2025 Sep;139:102979. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2025.102979. Epub 2025 Jun 14. Cancer Treat Rev. 2025. PMID: 40540857 Review.
-
New insight in early detection and precision medicine in small cell lung cancer: liquid biopsy as innovative clinical tool.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2025 Sep;62(6):404-428. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2025.2493121. Epub 2025 May 26. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2025. PMID: 40418084 Review.
-
Colorectal cancer: Application of selected liquid biopsy markers.Pol Przegl Chir. 2025 Mar 25;97(4):59-64. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0055.0608. Pol Przegl Chir. 2025. PMID: 40679021 Review.
-
Cancer in a drop: Advances in liquid biopsy in 2024.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2025 Sep;213:104776. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2025.104776. Epub 2025 May 28. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2025. PMID: 40447209 Review.
-
Recent advances in liquid biopsy for precision oncology: emerging biomarkers and clinical applications in lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2025 Aug 5:1-19. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2542051. Online ahead of print. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40762271 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

