Evaluation of Ultrasonic Spray Method for Application of Sirolimus-Eluting Coating on Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffolds
- PMID: 40806774
- PMCID: PMC12347766
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157649
Evaluation of Ultrasonic Spray Method for Application of Sirolimus-Eluting Coating on Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffolds
Abstract
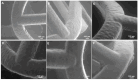
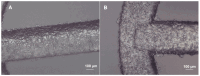
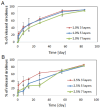
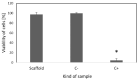
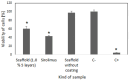
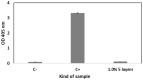
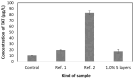
Restenosis is the main cause of failure after stent implantation during angioplasty. The localized, sustained delivery of an antirestenotic drug may reduce smooth muscle cell (SMCs) proliferation and thereby limit neointimal hyperplasia. The aim of this study was to develop degradable sirolimus-eluting polymer coatings that can be applied on bioresorbable polymer-based scaffolds via an ultrasonic coating system. This is a novel approach because the detailed analysis of the coating procedure on bioresorbable polymeric scaffolds with the use of an ultrasonic system has not been reported thus far. It has been observed that the ultrasonic technique facilitates formation of a smooth coating, well-integrated with the scaffold. However, the drug dose is affected by the concentration of the coating solution and the number of layers. Therefore, these parameters can be used for tailoring the drug dose and release process. Although all types of the developed coatings provided sirolimus elution for at least 3 months, a more uniform, diffusion-controlled release profile was observed from coatings obtained from the 1.0% polymeric solution. The released drug showed antiproliferative activity against vascular SMCs, without any hemolytic or thrombogenic effects. The results of the study may be advantageous for further progress in the development and medical translation of polymeric vascular scaffolds with antirestenotic activity.
Keywords: biodegradable vascular scaffolds; restenosis; sirolimus; stent coating; ultrasonic spray coating.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(26):1-149. doi: 10.3310/hta5260. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701099
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Diffusion of eHealth: Making Universal Health Coverage Achievable: Report of The Third Global Survey on eHealth. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Strohbach A., Busch R. Polymers for Cardiovascular Stent Coatings. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015;2015:782653. doi: 10.1155/2015/782653. - DOI
-
- Ono M., Takahashi K., Gao C., Kawashima H., Wu X., Hara H., Wang R., Wykrzykowska J.J., Piek J.J., Sharif F., et al. The state-of-the-art coronary stent with crystallized sirolimus: The MiStent technology and its clinical program. Future Cardiol. 2021;17:593–607. doi: 10.2217/fca-2020-0063. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mattke S., Hanson M., Dallmann A.C., Bentele M. Health Economic Evaluation of an Ultrathin, Bioresorbable-Polymer Sirolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent Compared to a Thin, Durable-Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stent. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2019;20:752–757. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2018.11.006. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

