Comparative Analysis of Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers Across Multiple Antiseizure Medications: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of 1782 Patients
- PMID: 40806813
- PMCID: PMC12347507
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14155190
Comparative Analysis of Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers Across Multiple Antiseizure Medications: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of 1782 Patients
Abstract
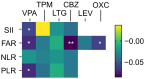
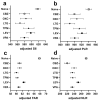
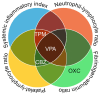
Background/Objectives: The aim of this study was to elucidate the associations between the use of various ASMs and systemic anti-inflammatory effects in a single large cohort using routine blood tests. Methods: Patients who underwent blood tests within three months of their first visit to our clinic were included. The systemic inflammatory index (SII, platelet × neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio), neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and fibrinogen-albumin ratio (FAR) were compared across specific ASMs. Data from a total of 1782 patients with epilepsy were analyzed. Results: Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that valproate use was significantly associated with lower SII, PLR, and FAR values. Additionally, carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine use were associated with the FAR, whereas topiramate use was associated with the PLR. When a dichotomized category for each inflammatory marker was used, dividing the lowest quartile and the other quartiles, VPA use was significantly associated with all four markers. Topiramate use was associated with lower SII, NLR, and PLR values, and carbamazepine use was associated with lower SII, FAR, and PLR values. Conclusions: These findings highlight the closer association between valproate, compared to other ASMs, and systemic inflammatory responses. These findings may offer valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of the therapeutic effects of valproate.
Keywords: antiseizure medication; carbamazepine; inflammation markers; topiramate; valproate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Predictive value of systemic inflammatory indices for perinatal outcomes following cervical cerclage: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jul 10;25(1):750. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07888-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40640782 Free PMC article.
-
Monotherapy treatment of epilepsy in pregnancy: congenital malformation outcomes in the child.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 29;8(8):CD010224. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010224.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37647086 Free PMC article.
-
Antiepileptic drug monotherapy for epilepsy: a network meta-analysis of individual participant data.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 15;12(12):CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 1;4:CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub4. PMID: 29243813 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antiepileptic drug monotherapy for epilepsy: a network meta-analysis of individual participant data.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 29;6(6):CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 15;12:CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub3. PMID: 28661008 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Fan M., Tang J., Du W., Du Y.F., Liu H.J. Systemic immunoinflammatory index and prognostic nutrition index for predicting pathologic responses of patients with advanced gastric cancer after neoadjuvant therapy for advanced gastric cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2024;14:3922–3934. doi: 10.62347/PAYM2267. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muhammad S., Fischer I., Naderi S., Faghih Jouibari M., Abdolreza S., Karimialavijeh E., Aslzadeh S., Mashayekhi M., Zojaji M., Kahlert U.D., et al. Systemic Inflammatory Index Is a Novel Predictor of Intubation Requirement and Mortality after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pathogens. 2021;10:58. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10010058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

