Advancing DIEP Flap Surgery: Robotic-Assisted Harvest Reduces Pain and Narcotic Use
- PMID: 40806826
- PMCID: PMC12346951
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14155204
Advancing DIEP Flap Surgery: Robotic-Assisted Harvest Reduces Pain and Narcotic Use
Abstract
Background: Robotic deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) flap surgery is a technique used for autologous breast reconstruction to maintain the integrity of the rectus abdominis muscle while also utilizing robotic assistance for flap harvest. This study assesses postoperative outcomes of patients undergoing robotic DIEP flap reconstruction through the measurement of postoperative pain, narcotics use, and antiemetic usage. Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed for patients undergoing robotic DIEP flap breast reconstruction between March 2024 and March 2025. Postoperative pain scores (1-10 scale), narcotics usage (measured in oral morphine equivalents), antiemetic usage, and complications were recorded. Patient outcomes were compared to a control group of 40 patients who had undergone abdominal-based free flap breast reconstruction. Results: Overall, 14 patients underwent robotic DIEP flap breast reconstruction, representing 24 breasts. The average patient age was 56.5 (range: 30-73). Ten patients underwent bilateral breast reconstruction, and four underwent unilateral breast reconstruction. The average length of stay postoperatively was 4.86 days (±1.23 days), and the return of bowel function occurred in 1.29 days (±0.47 days). No patients experienced an unplanned return to the OR or flap failure. Average pain scores on postoperative day 1 (POD1), 2 (POD2), and 3 (POD3) were 4.0 (±0.6), 3.4 (±0.6), and 2.93 (±0.5), respectively. Average antiemetic usage totalled 1.25 doses (±0.25). Average daily OME use was 27.7 (±5.0) for POD1, 25.96 (±6.3) for POD2, and 21.23 (±7.11) for POD3. This averaged to a total hospital OME use of 74.9 (±15.7) per patient. Patients undergoing robotic DIEP flap reconstruction required a significantly lower narcotics dosage, as well as a lower antiemetic dosage, during the first three days postoperatively compared to the control abdominal free flap group. Average pain scores in the robotic DIEP flap reconstruction patient group were also significantly decreased, specifically in POD2 and POD3. Conclusions: The robotic DIEP flap offers advantages in autologous breast reconstruction compared to other abdominal free flap reconstructive methods. In this limited retrospective study, the use of the robotic DIEP flap lowers chances of flap failure and complications, while also improving narcotics use, antiemetic use, and postoperative pain.
Keywords: autologous breast reconstruction; breast reconstruction; postoperative narcotics use; robotic deep inferior epigastric perforator flap.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
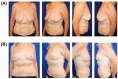
References
-
- Breast Cancer. [(accessed on 30 March 2025)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer.
-
- Franceschini G., Martin Sanchez A., Di Leone A., Magno S., Moschella F., Accetta C., Masetti R. New trends in breast cancer surgery: A therapeutic approach increasingly efficacy and respectful of the patient. Il G. Chir. J. Ital. Assoc. Hosp. Surg. 2015;36:145–152. doi: 10.11138/gchir/2015.36.4.145. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

