Impact of Bilateral GPi Deep Brain Stimulation on Dystonia, Functional Outcomes, and Caregiver Burden in Patients with Dystonic Cerebral Palsy
- PMID: 40807004
- PMCID: PMC12348014
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14155382
Impact of Bilateral GPi Deep Brain Stimulation on Dystonia, Functional Outcomes, and Caregiver Burden in Patients with Dystonic Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
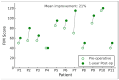
Background: Dystonic cerebral palsy (DCP) is a complex, disabling manifestation of secondary dystonia, which significantly impacts motor function, quality of life, and well-being. Conventional pharmacologic therapies frequently do not relieve symptoms sufficiently. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the globus pallidus internal segment (GPi) has gained increasing attention as a neuromodulatory therapy for refractory dystonia. Still, the experience of the effect of GPi DBS treatment in adults with DCP has, until recently, been limited. Methods: We performed a retrospective, two-center case series of 11 adult patients with medically refractory DCP who underwent bilateral GPi-DBS. The clinical outcomes were evaluated based on the Burke-Fahn-Marsden Dystonia Rating Scale (BFMDRS), the Functional Independence Measure (FIM), the Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS), and the Caregiver Burden Scale (CBS). The assessments were done preoperatively and at 1-year follow-up. Changes in continuous variables were analyzed using paired t-tests. Results: At the 1-year follow-up, the mean BFMDRS score improved from 69.6 ± 27.6 to 54.3 ± 36.5 (p = 0.001), indicating a significant reduction in overall dystonia severity. Functional independence also improved, demonstrated by the rise in FIM scores from 65.3 ± 33.9 to 79.2 ± 43.4 (p = 0.006). Although GMFCS levels did not change in most patients (p = 0.125), the burden on caregivers decreased significantly, with CBS scores falling from 35.7 ± 18.8 to 32.0 ± 17.1 (p = 0.015). There were no surgical complications. Conclusions: In adults, bilateral GPi-DBS is a safe and effective intervention for DCP, improving motor control and increasing functional independence while decreasing caregiver burden. These findings lend support to its role in the multidisciplinary management of DCP.
Keywords: caregiver burden; deep brain stimulation; dystonic cerebral palsy; functional independence; globus pallidus internus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microelectrode recording-guided globus pallidus pars internus deep brain stimulation treats dystonia under general anaesthesia: a retrospective experience of one center.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2025 Jul 4;167(1):184. doi: 10.1007/s00701-025-06595-4. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2025. PMID: 40613822 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Motor outcomes in unilateral, bilateral rapid, and bilateral delayed staging deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2024 Nov;14(8):1614-1622. doi: 10.1177/1877718X241296014. Epub 2024 Dec 8. J Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 39957194
-
Deep brain stimulation for hemidystonia: A meta-analysis with individual patient data.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2023 Mar;108:105317. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2023.105317. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 36813584
-
Efficacy of pallidal stimulation in isolated dystonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Neurol. 2017 Apr;24(4):552-560. doi: 10.1111/ene.13255. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Eur J Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28186378 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

