The Effect of Heterogeneous Definitions of Massive Transfusion on Using Blood Component Thresholds to Predict Futility in Severely Bleeding Trauma Patients
- PMID: 40807047
- PMCID: PMC12347820
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14155426
The Effect of Heterogeneous Definitions of Massive Transfusion on Using Blood Component Thresholds to Predict Futility in Severely Bleeding Trauma Patients
Abstract
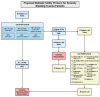
In the trauma resuscitation literature, there are inconsistent definitions of what constitutes massive transfusion and a unit of blood, complicating the use of transfusion cut-points to declare futility. This is problematic as it can lead to the inefficient use of blood products, further exacerbating current blood product shortages. Previous studies have used various transfusion cut-points per hour to define futility in retrospective analyses but have not accurately defined futility at the bedside due to patient survival even at large rates and volumes of blood transfused. In an attempt to use transfusion cut-points as a marker to help define futility, guidelines have been proposed to limit blood product waste in transfusions for severely bleeding trauma patients, such as Suspension of Transfusion and Other Procedures (STOP) for patients older than 15 and the Futility of Resuscitation Measure (FoRM), used to determine futility in patients older than 60. In an effort to construct effective bedside futile resuscitation criteria with 100% positive predictive value and specificity, this review proposes the use of specific blood component transfusion cut-points combined with parameters from both STOP and FoRM to allow for a comprehensive and accurate method of declaring futility in severely bleeding trauma patients.
Keywords: algorithm; blood component transfusion; futile resuscitation; hemorrhage; massive transfusion; medical futility; red blood cells; trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
E.E.M. and H.B.M. have received research grants from Haemonetics Corporation outside of the submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Doughty H., Green L., Callum J., Murphy M.F., National Blood Transfusion Committee Triage tool for the rationing of blood for massively bleeding patients during a severe national blood shortage: Guidance from the National Blood Transfusion Committee. Br. J. Haematol. 2020;191:340–346. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16736. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

