Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Achalasia Following Pneumatic Dilation Treatment: A Single Center Experience
- PMID: 40807069
- PMCID: PMC12347232
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14155448
Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Achalasia Following Pneumatic Dilation Treatment: A Single Center Experience
Abstract
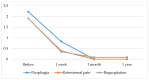
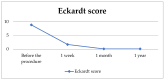
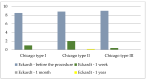
Background/Objectives: Pneumatic dilation (PD) is a widely used treatment modality in the management of achalasia. It is particularly relevant in regions where many centers lack access to advanced therapeutic modalities. Therefore, we aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of PD in our local region. Methods: This study retrospectively analyzed patients with achalasia that underwent PD from 1/2013 to 12/2019. The diagnosis of achalasia was established on the grounds of clinical symptoms, radiological and endoscopic findings, and esophageal manometry. Data on patient's clinical characteristics, dilation technique and postprocedural follow-up were collected and statistically analyzed. Procedure effectiveness was defined as the postprocedural Eckardt score ≤ 3. Results: PD significantly reduced frequency of dysphagia, regurgitation, and retrosternal pain (p < 0.001). Body-weight increased significantly one month and one year after the procedure (p < 0.001). The procedural success rate was 100%. No severe complications were reported. Conclusions: PD is an effective and safe treatment modality in the management of achalasia. The study limitations include a single center design with the small number of participants, not all of whom underwent manometry, gender disproportion, absence of non-responders, and a short follow-up.
Keywords: achalasia; dysphagia; pneumatic dilation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Efficacy of surgical or endoscopic treatment of idiopathic achalasia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jan;6(1):30-38. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30296-X. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33035470
-
Endoscopic pneumatic dilation versus botulinum toxin injection in the management of primary achalasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014(12):CD005046. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005046.pub3. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25485740 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Improvement in Health-related Quality of Life and Patient Satisfaction after Pneumatic Dilatation in Achalasia Patients.Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2025 Jan-Jun;15(1):54-57. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1472. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40718601 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources