Current Status of the Application of Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Conjugated Derivatives
- PMID: 40807245
- PMCID: PMC12348590
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30153070
Current Status of the Application of Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Conjugated Derivatives
Abstract
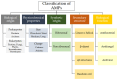
A significant issue in healthcare is the growing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant strains. Therefore, it is necessary to develop strategies for discovering new antibacterial compounds, either by identifying natural products or by designing semisynthetic or synthetic compounds with this property. In this context, a great deal of research has recently been carried out on antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), which are natural, amphipathic, low-molecular-weight molecules that act by altering the cell surface and/or interfering with cellular activities essential for life. Progress is also being made in developing strategies to enhance the activity of these compounds through their association with other molecules. In addition to identifying AMPs, it is essential to ensure that they maintain their integrity after passing through the digestive tract and exhibit adequate activity against their targets. Significant advances are being made in relation to analyzing various types of conjugates and carrier systems, such as nanoparticles, vesicles, hydrogels, and carbon nanotubes, among others. In this work, we review the current knowledge of different types of AMPs, their mechanisms of action, and strategies to improve performance.
Keywords: antibiotics; antimicrobial peptide conjugates; antimicrobial peptide nanostructures; antimicrobial peptides; antimicrobial resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Haq S.U., Ling W., Aqib A.I., Danmei H., Aleem M.T., Fatima M., Ahmad S., Gao F. Exploring the Intricacies of Antimicrobial Resistance: Understanding Mechanisms, Overcoming Challenges, and Pioneering Innovative Solutions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025;998:177511. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177511. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

