Quercetin Reduces Antinociceptive but Not the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Indomethacin, Ketorolac, and Celecoxib in Rats with Gout-like Pain
- PMID: 40807369
- PMCID: PMC12348991
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30153196
Quercetin Reduces Antinociceptive but Not the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Indomethacin, Ketorolac, and Celecoxib in Rats with Gout-like Pain
Abstract
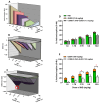
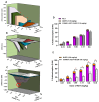
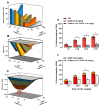
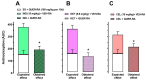
The objective of this study was to determine the pharmacological interaction of some common NSAIDs in the presence of quercetin (QUER). Indomethacin (IND), ketorolac (KET), or celecoxib (CEL) were assessed alone and in combination with QUER using experimental gout-arthritic pain and the carrageenan-induced edema test in rats to evaluate their antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects, respectively. The antinociceptive effect of each NSAID was also analyzed after the repeated administration of QUER for 10 days. Molecular docking analysis on COX-1/COX-2 with each drug was explored to analyze the pharmacological interaction. QUER produced minimal antinociceptive or anti-inflammatory effects on experimental gout-arthritic pain or on the carrageenan-induced edema in rats. Additionally, QUER reduced the antinociceptive effect of NSAIDs, mainly those COX-1 inhibitors (IND and KET), when they were combined. However, QUER did not modify the anti-inflammatory effect of these COX-1 inhibitors and slightly improved the anti-inflammatory effect of the COX-2 inhibitor (CEL). According to the docking analysis, COX-1 and COX-2 are likely implicated in these pharmacological interactions. In conclusion, QUER, a known bioactive natural product, may alter the antinociceptive efficacy of NSAIDs commonly used to relieve gout-like pain and suggests not using them together to prevent a negative therapeutic interaction in this effect.
Keywords: NSAIDs; gout pain; infra-additive interaction; natural products; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


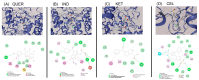
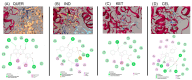
Similar articles
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for acute gout.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Sep 16;(9):CD010120. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010120.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 9;12:CD010120. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010120.pub3. PMID: 25225849 Updated.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for acute gout.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 9;12(12):CD010120. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010120.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34882311 Free PMC article.
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for axial spondyloarthritis (ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 17;2015(7):CD010952. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010952.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26186173 Free PMC article.
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents for treating cystoid macular edema following cataract surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 15;12(12):CD004239. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004239.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36520144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atanasov A.G., Waltenberger B., Pferschy-Wenzig E.M., Linder T., Wawrosch C., Uhrin P., Temml V., Wang L., Schwaiger S., Heiss E.H., et al. Discovery and resupply of pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015;3:1582–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

