Gastrointestinal Digestion Impact on Phenolics and Bioactivity of Tannat Grape Pomace Biscuits
- PMID: 40807422
- PMCID: PMC12348079
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30153247
Gastrointestinal Digestion Impact on Phenolics and Bioactivity of Tannat Grape Pomace Biscuits
Abstract
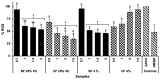
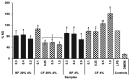
The search for natural sources of bioactive compounds with health-promoting properties has intensified in recent years. Among these, Tannat grape pomace (TGP), a primary byproduct of winemaking, stands out for its high phenolic content, although its bioactivity may be affected during gastrointestinal digestion. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of in vitro digestion on the antioxidant (ABTS, ORAC-FL, intracellular ROS inhibition), anti-diabetic (α-glucosidase inhibition), anti-obesity (lipase inhibition), and anti-inflammatory (NO inhibition) properties of five sugar-free biscuits formulated with varying percentages of TGP and sucralose. No significant differences were observed in the bioaccessible fractions (BFs, representing the compounds potentially released in the small intestine) between control biscuits and those enriched with TGP, suggesting limited release of phenolics at this stage. Conversely, the colonic fractions (CFs, simulating the material reaching the colon) from biscuits with higher TGP content exhibited greater bioactivities. HPLC-DAD-MS analysis of the CF from the biscuit containing 20% TGP and 4% sucralose revealed a high content of procyanidin trimers, indicating the persistence of these specific phenolic compounds after in vitro digestion. These findings suggest that TGP-enriched biscuits may deliver health benefits at the colonic level and support their potential application in the formulation of functional foods. Further microbiota and in vivo studies should be assessed to confirm the latter.
Keywords: bioaccessibility; bioactivity; biscuits; in vitro digestion; phenolic compounds; tannat grape pomace.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tannat grape pomace as an ingredient for potential functional biscuits: bioactive compound identification, in vitro bioactivity, food safety, and sensory evaluation.Front Nutr. 2023 Sep 7;10:1241105. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1241105. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37743913 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assessment of Phenolic Compounds from Encapsulated Grape Pomace Extract by Ionic Gelation.Molecules. 2023 Jul 7;28(13):5285. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135285. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446946 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Caponio G.R., Minervini F., Tamma G., Gambacorta G., De Angelis M. Promising Application of Grape Pomace and Its Agri-Food Valorization: Source of Bioactive Molecules with Beneficial Effects. Sustainability. 2023;15:9075. doi: 10.3390/su15119075. - DOI
-
- Da Silva C., Molin A.D., Ferrarini A., Boido E., Gaggero C., Delledonne M., Carrau F. The Tannat Genome: Unravelling Its Unique Characteristics. BIO Web Conf. 2019;12:01016. doi: 10.1051/bioconf/20191201016. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

