Standardization of Germinated Oat Extracts and Their Neuroprotective Effects Against Aβ1-42 Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
- PMID: 40807466
- PMCID: PMC12348729
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30153291
Standardization of Germinated Oat Extracts and Their Neuroprotective Effects Against Aβ1-42 Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
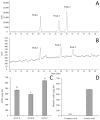
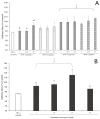
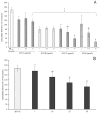
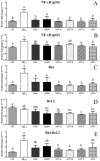
The present study aimed to standardize germinated oat extracts (GOEs) by profiling avenanthramides (AVNs) and phenolic acids and evaluate their neuroprotective effects against Aβ1-42-induced cytotoxicity in human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells. GOEs were standardized to contain 1652.56 ± 3.37 µg/g dry weight (dw) of total AVNs, including 468.52 ± 17.69 µg/g AVN A, 390.33 ± 10.26 µg/g AVN B, and 641.22 ± 13.89 µg/g AVN C, along with 490.03 ± 7.83 µg/g dw of ferulic acid, using a validated analytical method. Treatment with AVN C and GOEs significantly inhibited Aβ1-42-induced cytotoxicity (p < 0.05). Furthermore, both AVNs and GOEs markedly reduced Aβ1-42-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in SH-SY5Y cells, showing significant scavenging activity at concentrations of 25 μg/mL (AVNs) and 50 μg/mL (GOEs) (p < 0.05). RT-PCR analysis revealed that AVNs and GOEs effectively downregulated the expression of inflammation- and apoptosis-related genes triggered by Aβ1-42 exposure. These findings suggest that GOEs rich in AVNs may serve as a potential functional ingredient for enhancing memory function through the inhibition of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: Aβ1-42; avenanthramides; germinated oat extracts; human neuroblastoma cell; memory improvement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Avenanthramide C from underutilized oat glumes exhibits dual anti-oxidant and anti-thrombotic effects in oxidative damage and thrombosis models.Food Funct. 2025 Jul 1;16(13):5380-5392. doi: 10.1039/d5fo00366k. Food Funct. 2025. PMID: 40476819
-
The Neuroprotective Potential of Seed Extract from the Indian Trumpet Tree Against Amyloid Beta-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 29;26(13):6288. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136288. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650065 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Assessment of Cholinesterase Inhibition and Neuroprotective Effects of Elaeocarpus angustifolius Blume Against Amyloid-Beta Peptide-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y and BV-2 Cells.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jul 9;50(4):226. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04478-9. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40632335
-
Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Porcine Brain Enzyme Hydrolysate in Memory Impairment: Multi-Target Strategy Against Amyloid-β-Induced Neurotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 24;26(13):6030. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136030. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649809 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic acid attenuates amyloid β1-42-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibits the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells.Neurochem Int. 2024 Sep;178:105772. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105772. Epub 2024 May 22. Neurochem Int. 2024. PMID: 38789043
References
-
- Peng Y., Tao H.X., Wang S.P., Xiao J.B., Wang Y.T., Su H.X. Dietary intervention with edible medicinal plants and derived products for prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: A compendium of time-tested strategy. J. Funct. Foods. 2021;81:104463. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104463. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

