Metabolic Master Switch: Pyruvate Carboxylase Fuels Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Foodborne Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 40807502
- PMCID: PMC12346120
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14152566
Metabolic Master Switch: Pyruvate Carboxylase Fuels Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Foodborne Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
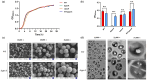
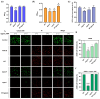
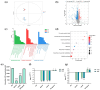
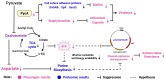
Staphylococcus aureus, a major cause of foodborne illness globally, presents significant challenges due to its multidrug resistance and biofilm-forming capabilities. Pyruvate carboxylase (PycA), a metabolic master switch linking glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a potential target for controlling S. aureus. In this study, a pycA mutant was constructed and analyzed using phenotypic assays and proteomics to investigate its role in virulence and antimicrobial resistance. The results showed that deletion of pycA in the foodborne methicillin-resistant strain ATCC BAA1717 resulted in a 4- to 1024-fold reduction in resistance to β-lactams, aminoglycosides, and macrolides; a 23.24% impairment in biofilm formation; and a 22.32% decrease in staphyloxanthin production, a key antioxidant essential for survival in oxidative food environments. Proteomic analysis revealed downregulation of the TCA cycle, purine biosynthesis, surface adhesins (FnbA/B, SasG), and β-lactamase (BlaZ), linking PycA-mediated metabolism to phenotypes relevant to food safety. These findings underscore the importance of PycA as a metabolic regulator crucial for S. aureus resilience in food systems, suggesting novel strategies to combat foodborne staphylococcal infections through metabolic interference.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; TCA cycle; antimicrobial resistance; biofilm; purine metabolism; pyruvate carboxylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial, personal, or professional interests that could influence the content or evaluation of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Sivakumar M., Dubal Z.B., Kumar A., Bhilegaonkar K., Vinodh Kumar O.R., Kumar S., Kadwalia A., Shagufta B., Grace M.R., Ramees T.P., et al. Virulent methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in street vended foods. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019;56:1116–1126. doi: 10.1007/s13197-019-03572-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Noskin G.A., Rubin R.J., Schentag J.J., Kluytmans J., Hedblom E.C., Smulders M., Lapetina E., Gemmen E. The Burden of Staphylococcus aureus Infections on Hospitals in the United States: An Analysis of the 2000 and 2001 Nationwide Inpatient Sample Database. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005;165:1756–1761. doi: 10.1001/archinte.165.15.1756. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

