Antimicrobial Properties of Thermally Processed Oyster Shell Powder for Use as Calcium Supplement
- PMID: 40807516
- PMCID: PMC12346358
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14152579
Antimicrobial Properties of Thermally Processed Oyster Shell Powder for Use as Calcium Supplement
Abstract
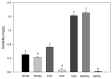
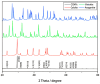
Oyster shells, though rich in calcium, are mostly discarded and contribute to environmental issues. Developing calcium-based materials with antimicrobial functionality offers a promising solution. However, their low bioavailability limits their direct use, requiring processing to enhance their applicability. Therefore, this study aims to evaluate the physicochemical properties and antimicrobial activity of thermally processed pulverized oyster shells (TPOS) and citric acid-treated TPOS (TPOSc) compared with those of fibrous calcium carbonate (FCC) and coral-derived calcium product (CCP), which are used as reference materials. The solubility values were 0.7 mg/g for FCC, 0.5 mg/g for TPOS, 0.4 mg/g for TPOSc, and 0.05 mg/g for CCP. The average particle sizes were 476 (FCC), 1000 (TPOS and TPOSc), and 1981 nm (CCP). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses revealed calcium ion release and structural changes in TPOS and TPOSc. Antibacterial testing further confirmed that these samples exhibited significant antimicrobial activity. Furthermore, to assess their practical applicability, TPOS and TPOSc samples with antimicrobial properties were incorporated into rice cakes. All samples retained antimicrobial activity at 0.3 wt%, while higher concentrations led to deterioration in their textural properties. These findings support the potential of thermally processed oyster shell powders for food applications that require microbial control with minimal impact on product quality.
Keywords: antimicrobial; bioavailability; calcium; oyster shells; thermal processing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
-
The quantity, quality and findings of network meta-analyses evaluating the effectiveness of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss: a scoping review.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Jun 25:1-73. doi: 10.3310/SKHT8119. Online ahead of print. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40580049 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellei P., Torres I., Solstad R., Flores-Colen I. Potential Use of Oyster Shell Waste in the Composition of Construction Composites: A Review. Buildings. 2023;13:1546. doi: 10.3390/buildings13061546. - DOI
-
- Silva T.H., Mesquita-Guimarães J., Henriques B., Silva F.S., Fredel M.C. The potential use of oyster shell waste in new value-added by-product. Resources. 2019;8:13. doi: 10.3390/resources8010013. - DOI
-
- Ke H., Ma R., Liu X., Xie Y., Chen J. Highly effective peptide-calcium chelate prepared from aquatic products processing wastes: Stickwater and oyster shells. Lwt. 2022;168:113947. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113947. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

