Fermentation to Increase the Value of Roasted Coffee Silverskin as a Functional Food Ingredient
- PMID: 40807545
- PMCID: PMC12346125
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14152608
Fermentation to Increase the Value of Roasted Coffee Silverskin as a Functional Food Ingredient
Abstract
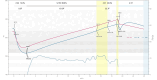
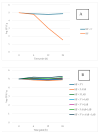
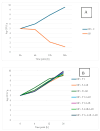
Roasted coffee silverskin (RCSS) is a by-product of coffee production characterized by its content of phenolic compounds, both free and bound to macromolecules. In this study, RCSS was fermented to release these compounds and consequently increase its value as a functional food ingredient. Fermentation was carried out using yeast, acetic acid bacteria, and lactic acid bacteria, either as single strains or as a designed microbial consortium. The latter included Saccharomycodes ludwigii, Gluconobacter oxydans, and Levilactobacillus brevis, mimicking a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast commonly used in kombucha fermentation (SCOBY). This symbiotic microbial culture consortium demonstrated notable efficacy, significantly enhancing the total phenolic content in RCSS, with values reaching 14.15 mg GAE/g as determined by the Folin-Ciocalteu assay and 7.12 mg GAE/g according to the Fast Blue BB method. Antioxidant capacity improved by approximately 28% (ABTS) and 20% (DPPH). Moreover, the fermented RCSS supported the viability of probiotic strains (Saccharomyces boulardii SB01 and Levilactobacillus brevis ŁOCK 1152) under simulated intestinal conditions. These results suggest that RCSS, particularly after fermentation with a full symbiotic microbial culture consortium, has strong potential as a clean label, zero-waste functional food ingredient.
Keywords: antioxidant capacity; clean label; functional food ingredients; microbial fermentation; phenolic compounds; prebiotic potential; probiotic viability; roasted coffee silverskin; symbiotic microbial culture consortium; zero waste.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Kombucha Fermentation With Dried Starter Cultures: A Strategy for Microbial Stabilization via Spray and Freeze Drying.J Food Sci. 2025 Aug;90(8):e70474. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.70474. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40785438 Free PMC article.
-
Oak Acorns as Functional Foods: Antioxidant Potential and Safety Assessment.Foods. 2025 Jul 16;14(14):2486. doi: 10.3390/foods14142486. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40724307 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional labelling for healthier food or non-alcoholic drink purchasing and consumption.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 27;2(2):CD009315. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009315.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29482264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galanakis C.M. Sustainable Food Systems from Agriculture to Industry. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. Food Waste Recovery: Prospects and Opportunities; pp. 401–419.
-
- Sloan A.E. Food expo highlights clean labels and functional foods. Food Technol. 2011;65:48–51.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

