Development of Supplements of Calcium Microencapsulated with Brewer's Spent Yeast Mannoproteins-Study of Gastrointestinal and Colonic Bioaccessibility
- PMID: 40807569
- PMCID: PMC12346725
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14152632
Development of Supplements of Calcium Microencapsulated with Brewer's Spent Yeast Mannoproteins-Study of Gastrointestinal and Colonic Bioaccessibility
Abstract
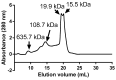
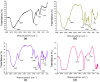
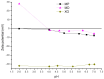
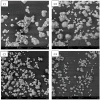
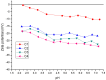
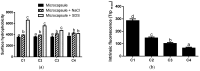
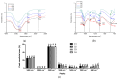
Calcium microcapsules were developed by spray-drying using mannoproteins (MPs) extracted from brewer's spent yeast, xanthan gum (XG), and maltodextrin as encapsulating materials. The formulas included 11 g of calcium, 24 g of MP, and 0, 2, 4, or 8 g of XG 100 g-1 solids, obtaining C1, C2, C3, and C4 microcapsules, respectively. Maltodextrin was added to complete 100 g of solids. Calcium intestinal (IB), colonic (CB), and total bioaccessibility (TB) were estimated after a simulated gastrointestinal digestion followed by in vitro colonic fermentation. The macromolecules of microcapsules interacted by ionic and hydrophobic forces. Microcapsules C1 and C2 showed a spherical shape. However, the addition of XG to the formulation contributed to the formation of concavities in the microcapsules. All microcapsules had higher IB than the control (CaCl2), probably due to the calcium-chelating peptides dialyzed from MP. Moreover, C1 and C2 showed the highest IB values (≈23%). However, C3 and C4 showed the highest CB values (≈11%), attributing this effect to the short-chain fatty acids produced during colonic fermentation. Finally, C1 and C2 showed the highest TB (31.8 ± 0.1 and 32.0 ± 0.4%, respectively). The use of MP allowed for obtaining a supplement with high calcium bioaccessibility.
Keywords: Saccharomyces cerevisiae; calcium dialyzability; glycoproteins; microcapsules; short-chain fatty acids; spray-drying.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- da Silva Araújo V.B., de Melo A.N.F., Costa A.G., Castro-Gomez R.H., Madruga M.S., de Souza E.L., Magnani M. Followed extraction of β-glucan and mannoprotein from spent brewer’s yeast (Saccharomyces uvarum) and application of the obtained mannoprotein as a stabilizer in mayonnaise. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014;23:164–170. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2013.12.013. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

