Advancing Food Safety Surveillance: Rapid and Sensitive Biosensing Technologies for Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria
- PMID: 40807591
- PMCID: PMC12346877
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14152654
Advancing Food Safety Surveillance: Rapid and Sensitive Biosensing Technologies for Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria
Abstract
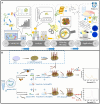
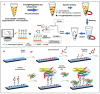
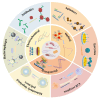
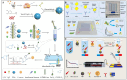
Foodborne pathogenic bacteria critically threaten public health and food industry sustainability, serving as a predominant trigger of food contamination incidents. To mitigate these risks, the development of rapid, sensitive, and highly specific detection technologies is essential for early warning and effective control of foodborne diseases. In recent years, biosensors have gained prominence as a cutting-edge tool for detecting foodborne pathogens, owing to their operational simplicity, rapid response, high sensitivity, and suitability for on-site applications. This review provides a comprehensive evaluation of critical biorecognition elements, such as antibodies, aptamers, nucleic acids, enzymes, cell receptors, molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs), and bacteriophages. We highlight their design strategies, recent advancements, and pivotal contributions to improving detection specificity and sensitivity. Additionally, we systematically examine mainstream biosensor-based detection technologies, with a focus on three dominant types: electrochemical biosensors, optical biosensors, and piezoelectric biosensors. For each category, we analyze its fundamental principles, structural features, and practical applications in food safety monitoring. Finally, this review identifies future research priorities, including multiplex target detection, enhanced processing of complex samples, commercialization, and scalable deployment of biosensors. These advancements are expected to bridge the gap between laboratory research and real-world food safety surveillance, fostering more robust and practical solutions.
Keywords: biorecognition elements; biosensors; food safety monitoring; foodborne pathogenic bacteria; rapid detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Innovations in aptamer-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria: Recent advances and perspective.Talanta. 2025 Dec 1;295:128330. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2025.128330. Epub 2025 May 14. Talanta. 2025. PMID: 40388877 Review.
-
Strategic Detection of Escherichia coli in the Poultry Industry: Food Safety Challenges, One Health Approaches, and Advances in Biosensor Technologies.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jul 1;15(7):419. doi: 10.3390/bios15070419. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40710069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development, fabrication, and applications of laser-induced graphene-based biosensors in food and dairy sectors.Mikrochim Acta. 2025 Aug 4;192(9):554. doi: 10.1007/s00604-025-07395-4. Mikrochim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40760054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Detection Methods for Staphylococcus aureus and Its Enterotoxins in Food: From Traditional to Emerging Technologies.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;17(7):319. doi: 10.3390/toxins17070319. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40711131 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deng R., Bai J., Yang H., Ren Y., He Q., Lu Y. Nanotechnology-Leveraged Nucleic Acid Amplification for Foodborne Pathogen Detection. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024;506:215745. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2024.215745. - DOI
-
- Ali S.S., Moawad M.S., Hussein M.A., Azab M., Abdelkarim E.A., Badr A., Sun J., Khalil M. Efficacy of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Novel Antimicrobial Agents against Multi-Drug and Multi-Virulent Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Retail Raw Chicken Meat and Giblets. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021;344:109116. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109116. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

