Influence of Various Cooking Methods on Selenium Concentrations in Commonly Consumed Seafood Species in Thailand
- PMID: 40807636
- PMCID: PMC12346270
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14152700
Influence of Various Cooking Methods on Selenium Concentrations in Commonly Consumed Seafood Species in Thailand
Abstract
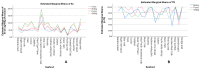
Selenium (Se) is an important trace element in our body; however, food composition data remain limited due to analytical challenges and interferences. Seafood, abundant in Thailand, is recognized as a rich source of Se. This study aimed to expand knowledge on Se content in seafood prepared using traditional Thai cooking methods. Twenty seafood species were selected and prepared by boiling, frying, and grilling. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Triple Quadrupole-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) was used to analyze total Se contents in selected seafood species. Results revealed significant variation in Se content across species and cooking methods. The Indo-Pacific horseshoe crab showed the highest Se concentration, with fried samples reaching 193.9 μg/100 g. Se concentrations were in the range of 8.6-155.5 μg/100 g (fresh), 14.3-106.6 μg/100 g (boiled), 17.3-193.9 μg/100 g (fried), and 7.3-160.1 μg/100 g (grilled). Results found significant effects of species and cooking method on Se content (p < 0.05). Fried seafood exhibited the highest estimated marginal mean Se concentration (a 78.8 μg/100 g edible portion), significantly higher than other methods. True retention (%TR) of Se ranged from 40.4% to 100%, depending on species and method. Bigfin reef squid, wedge shell, and silver pomfret showed the highest %TR (100%), while splendid squid exhibited the lowest (52.5%). Significant interaction effects on %TR were also observed (p < 0.05). Fried seafood had the highest mean %TR (88.8%), followed by grilled (82.1%) and boiled (79.7%). These findings highlight the effects of both species and cooking method on Se retention, emphasizing the nutritional value of selected seafood in preserving bioavailable Se after cooking.
Keywords: food analysis; seafood; selenium; trace elements; true retention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Potassium quantification and sensory analysis in plant food cooking processes in heart disease patients.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2025 Jul 17;69:350-357. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2025.07.003. Online ahead of print. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2025. PMID: 40681108
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials