Potential of Plant-Based Oil Processing Wastes/By-Products as an Alternative Source of Bioactive Compounds in the Food Industry
- PMID: 40807655
- PMCID: PMC12345653
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14152718
Potential of Plant-Based Oil Processing Wastes/By-Products as an Alternative Source of Bioactive Compounds in the Food Industry
Abstract
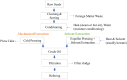
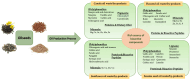
The plant-based oil industry contributes significantly to food waste/by-products in the form of underutilized biomass, including oil pomace, cake/meal, seeds, peels, wastewater, etc. These waste/by-products contain a significant quantity of nutritious and bioactive compounds (phenolics, lignans, flavonoids, dietary fiber, proteins, and essential minerals) with proven health-promoting effects. The utilization of them as natural, cost-effective, and food-grade functional ingredients in novel food formulations holds considerable potential. This review highlights the potential of waste/by-products generated during plant-based oil processing as a promising source of bioactive compounds and covers systematic research, including recent studies focusing on innovative extraction and processing techniques. It also sheds light on their promising potential for valorization as food ingredients, with a focus on specific examples of food fortification. Furthermore, the potential for value creation in the food industry is emphasized, taking into account associated challenges and limitations, as well as future perspectives. Overall, the current information suggests that the valorization of plant-based oil industry waste and by-products for use in the food industry could substantially reduce malnutrition and poverty, generate favorable health outcomes, mitigate environmental concerns, and enhance economic profit in a sustainable way by developing health-promoting, environmentally sustainable food systems.
Keywords: agro-industrial residues; antioxidant-rich; edible oil processing waste; functional food ingredients; oilcake utilization; waste/by-product valorization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
A Review on Innovative Biotechnological Approaches for the Upcycling of Citrus Fruit Waste to Obtain Value-Added Bioproducts§.Food Technol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun;63(2):238-261. doi: 10.17113/ftb.63.02.25.8735. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40735162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wood Waste Valorization and Classification Approaches: A systematic review.Open Res Eur. 2025 May 6;5:5. doi: 10.12688/openreseurope.18862.2. eCollection 2025. Open Res Eur. 2025. PMID: 40438563 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Human Health Through Nutrient and Bioactive Compound Recovery from Agri-Food By-Products: A Decade of Progress.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 31;17(15):2528. doi: 10.3390/nu17152528. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Valorization of Food Waste: Extracting Bioactive Compounds for Sustainable Health and Environmental Solutions.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 11;14(6):714. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060714. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563346 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sharma P., Gaur V.K., Gupta S., Varjani S., Pandey A., Gnansounou E., You S., Ngo H.H., Wong J.W.C. Trends in Mitigation of Industrial Waste: Global Health Hazards, Environmental Implications and Waste Derived Economy for Environmental Sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2022;811:152357. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152357. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Martins S.H.F., Pontes K.V., Fialho R.L., Fakhouri F.M. Extraction and Characterization of the Starch Present in the Avocado Seed (Persea Americana Mill) for Future Applications. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022;8:100303. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2022.100303. - DOI
-
- Socas-Rodríguez B., Álvarez-Rivera G., Valdés A., Ibáñez E., Cifuentes A. Food By-Products and Food Wastes: Are They Safe Enough for Their Valorization? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021;114:133–147. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.002. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

