Bioactive Compounds, Technological Advances, and Sustainable Applications of Avocado (Persea americana Mill.): A Critical Review
- PMID: 40807683
- PMCID: PMC12346796
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14152746
Bioactive Compounds, Technological Advances, and Sustainable Applications of Avocado (Persea americana Mill.): A Critical Review
Abstract
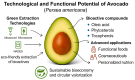
Avocado (Persea americana), originally from Mesoamerica, has emerged as a focus of intense scientific and industrial interest due to its unique combination of nutritional richness, bioactive potential, and technological versatility. Its pulp, widely consumed across the globe, is notably abundant in monounsaturated fatty acids, especially oleic acid, which can comprise over two-thirds of its lipid content. In addition, it provides significant levels of dietary fiber, fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E and K, carotenoids, tocopherols, and phytosterols like β-sitosterol. These constituents are consistently associated with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, glycemic regulatory, and cardioprotective effects, supported by a growing body of experimental and clinical evidence. This review offers a comprehensive and critical synthesis of the chemical composition and functional properties of avocado, with particular emphasis on its lipid profile, phenolic compounds, and phytosterols. It also explores recent advances in environmentally sustainable extraction techniques, including ultrasound-assisted and microwave-assisted processes, as well as the application of natural deep eutectic solvents. These technologies have demonstrated improved efficiency in recovering bioactives while aligning with the principles of green chemistry. The use of avocado-derived ingredients in nanostructured delivery systems and their incorporation into functional foods, cosmetics, and health-promoting formulations is discussed in detail. Additionally, the potential of native cultivars and the application of precision nutrition strategies are identified as promising avenues for future innovation. Taken together, the findings underscore the avocado's relevance as a high-value matrix for sustainable development. Future research should focus on optimizing extraction protocols, clarifying pharmacokinetic behavior, and ensuring long-term safety in diverse applications.
Keywords: Persea americana; bioactive lipids; cosmeceuticals; functional foods; green extraction technologies; nanostructured systems; nutraceuticals; phytochemicals; phytosterols; precision nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
The role of avocado plant and its derivatives in the management of diabetes mellitus: a natural approach to glycemic control.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025 Jan 4;24(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s40200-024-01551-y. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 39764472 Review.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Sustainable Valorization of Olive Oil By-Products: Green Extraction of Phytochemicals, Encapsulation Strategies, and Food Applications.J Food Sci. 2025 Jul;90(7):e70412. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.70412. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40711829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing Human Health Through Nutrient and Bioactive Compound Recovery from Agri-Food By-Products: A Decade of Progress.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 31;17(15):2528. doi: 10.3390/nu17152528. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Monique A.M., Abeles L., Blithe K., Packert E., Anseth E. Effects of partial butter replacement with avocado puree in chocolate muffins. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2022;6((Suppl. 1)):523. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzac077.026. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

