Barefoot Footprint Detection Algorithm Based on YOLOv8-StarNet
- PMID: 40807744
- PMCID: PMC12349430
- DOI: 10.3390/s25154578
Barefoot Footprint Detection Algorithm Based on YOLOv8-StarNet
Abstract
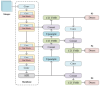
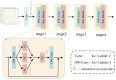
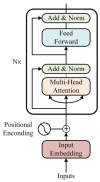
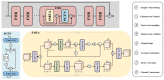
This study proposes an optimized footprint recognition model based on an enhanced StarNet architecture for biometric identification in the security, medical, and criminal investigation fields. Conventional image recognition algorithms exhibit limitations in processing barefoot footprint images characterized by concentrated feature distributions and rich texture patterns. To address this, our framework integrates an improved StarNet into the backbone of YOLOv8 architecture. Leveraging the unique advantages of element-wise multiplication, the redesigned backbone efficiently maps inputs to a high-dimensional nonlinear feature space without increasing channel dimensions, achieving enhanced representational capacity with low computational latency. Subsequently, an Encoder layer facilitates feature interaction within the backbone through multi-scale feature fusion and attention mechanisms, effectively extracting rich semantic information while maintaining computational efficiency. In the feature fusion part, a feature modulation block processes multi-scale features by synergistically combining global and local information, thereby reducing redundant computations and decreasing both parameter count and computational complexity to achieve model lightweighting. Experimental evaluations on a proprietary barefoot footprint dataset demonstrate that the proposed model exhibits significant advantages in terms of parameter efficiency, recognition accuracy, and computational complexity. The number of parameters has been reduced by 0.73 million, further improving the model's speed. Gflops has been reduced by 1.5, lowering the performance requirements for computational hardware during model deployment. Recognition accuracy has reached 99.5%, with further improvements in model precision. Future research will explore how to capture shoeprint images with complex backgrounds from shoes worn at crime scenes, aiming to further enhance the model's recognition capabilities in more forensic scenarios.
Keywords: StarNet; YOLOv8; barefoot footprint; criminal investigation; element-wise multiplication; feature fusion; lightweighting; low hardware requirements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang K., Guo W., Wang Z., Han W. Research review on barefoot footprint identification. J. Comput. Sci. Explor. 2024;18:44–57.
-
- Simonyan K., Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition; Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR); San Diego, CA, USA. 7–9 May 2015.
-
- LeCun Y., Bottou L., Bengio Y., Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE. 1998;86:2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791. - DOI
-
- He K., Zhang X., Ren S., Sun J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv. 20151512.03385
-
- LeCun Y. Generalization and Network Design Strategies. In: Pfeifer R., Schreter Z., Fogelman F., editors. Connectionism in Perspective. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 1989. pp. 143–155.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources