Optimization of a Navigation System for Autonomous Charging of Intelligent Vehicles Based on the Bidirectional A* Algorithm and YOLOv11n Model
- PMID: 40807745
- PMCID: PMC12349329
- DOI: 10.3390/s25154577
Optimization of a Navigation System for Autonomous Charging of Intelligent Vehicles Based on the Bidirectional A* Algorithm and YOLOv11n Model
Abstract
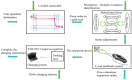
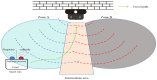
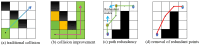
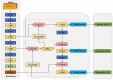
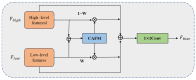
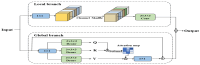
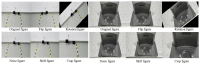
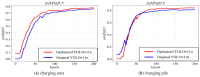
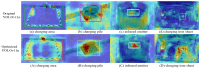
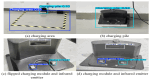
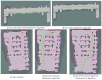
Aiming to enable intelligent vehicles to achieve autonomous charging under low-battery conditions, this paper presents a navigation system for autonomous charging that integrates an improved bidirectional A* algorithm for path planning and an optimized YOLOv11n model for visual recognition. The system utilizes the improved bidirectional A* algorithm to generate collision-free paths from the starting point to the charging area, dynamically adjusting the heuristic function by combining node-target distance and search iterations to optimize bidirectional search weights, pruning expanded nodes via a greedy strategy and smoothing paths into cubic Bézier curves for practical vehicle motion. For precise localization of charging areas and piles, the YOLOv11n model is enhanced with a CAFMFusion mechanism to bridge semantic gaps between shallow and deep features, enabling effective local-global feature fusion and improving detection accuracy. Experimental evaluations in long corridors and complex indoor environments showed that the improved bidirectional A* algorithm outperforms the traditional improved A* algorithm in all metrics, particularly in that it reduces computation time significantly while maintaining robustness in symmetric/non-symmetric and dynamic/non-dynamic scenarios. The optimized YOLOv11n model achieves state-of-the-art precision (P) and mAP@0.5 compared to YOLOv5, YOLOv8n, and the baseline model, with a minor 0.9% recall (R) deficit compared to YOLOv5 but more balanced overall performance and superior capability for small-object detection. By fusing the two improved modules, the proposed system successfully realizes autonomous charging navigation, providing an efficient solution for energy management in intelligent vehicles in real-world environments.
Keywords: ROS system; YOLOv11n; bidirectional A*; corridor environment; path planning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrated neural network framework for multi-object detection and recognition using UAV imagery.Front Neurorobot. 2025 Jul 30;19:1643011. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2025.1643011. eCollection 2025. Front Neurorobot. 2025. PMID: 40809070 Free PMC article.
-
I-YOLOv11n: A Lightweight and Efficient Small Target Detection Framework for UAV Aerial Images.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Aug 7;25(15):4857. doi: 10.3390/s25154857. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40808027 Free PMC article.
-
Research of UAV 3D path planning based on improved Dwarf mongoose algorithm with multiple strategies.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 24;15(1):26979. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11492-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40707532 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
PET-CT for assessing mediastinal lymph node involvement in patients with suspected resectable non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 13;2014(11):CD009519. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009519.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25393718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Su K.L., Liao Y.L., Lin S.P., Lin S.F. An interactive auto-recharging system for mobile robots. Int. J. Autom. Smart Technol. 2014;4:43–53. doi: 10.5875/ausmt.v4i1.197. - DOI
-
- Li S., Xu H., Ji Y., Cao R., Zhang M., Li H. Development of a following agricultural machinery automatic navigation system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019;158:335–344. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2019.02.019. - DOI
-
- Srivastava N., Singh H., Ikram M., Setia N., Sharma P., Raju V.S.P., Kampani S. Sustainable Vision-Based Navigation for Autonomous Electric Vehicle Charging; Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences: International Conference on Sustainable Green Energy Technologies (ICSGET 2024); Hyderabad, India. 14–15 June 2024.
-
- Zhang F., Liu J., Li Q. A shortest path optimization algorithm based on Dijkstra’s algorithm. Remote Sens. Inf. 2004;2:38–41.
-
- Tang G., Tang C., Claramunt C., Hu X., Zhou P. Geometric A-star algorithm: An improved A-star algorithm for AGV path planning in a port environment. IEEE Access. 2021;9:59196–59210. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3070054. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

