Advancements in Sensor Technology for Monitoring and Management of Chronic Coronary Syndrome
- PMID: 40807750
- PMCID: PMC12349277
- DOI: 10.3390/s25154585
Advancements in Sensor Technology for Monitoring and Management of Chronic Coronary Syndrome
Abstract
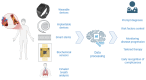
Chronic Coronary Syndrome (CCS) significantly impacts quality of life and increases the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, remaining the leading cause of mortality worldwide. The use of sensor technology in medicine is emerging as a promising approach to enhance the management and monitoring of patients across a wide range of diseases. Recent advancements in engineering and nanotechnology have enabled the development of ultra-small devices capable of collecting data on critical physiological parameters. Several sensors integrated in wearable and implantable devices, instruments for exhaled gas analysis, smart stents and tools capable of real time biochemical analysis have been developed, and some of them have demonstrated to be effective in CCS management. Their application in CCS could provide valuable insights into disease progression, ischemic events, and patient responses to therapy. Moreover, sensor technologies can support the personalization of treatment plans, enable early detection of disease exacerbations, and facilitate prompt interventions, potentially reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and unnecessary invasive diagnostic procedures such as coronary angiography. This review explores sensor integration in CCS care, highlighting technological advances, clinical potential, and implementation challenges.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; chronic coronary syndrome; coronary artery disease; device; sensor; technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Safiri S., Karamzad N., Singh K., Carson-Chahhoud K., Adams C., Nejadghaderi S.A., Almasi-Hashiani A., Sullman M.J.M., Mansournia M.A., Bragazzi N.L., et al. Burden of Ischemic Heart Disease and Its Attributable Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022;29:420–431. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwab213. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Virani S.S., Newby L.K., Arnold S.V., Bittner V., Brewer L.C., Demeter S.H., Dixon D.L., Fearon W.F., Hess B., Johnson H.M., et al. 2023 AHA/ACC/ACCP/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline for the Management of Patients With Chronic Coronary Disease: A Report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2023;148:e9–e119. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001168. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beck R.W., Riddlesworth T., Ruedy K., Ahmann A., Bergenstal R., Haller S., Kollman C., Kruger D., McGill J.B., Polonsky W., et al. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Injections: The DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017;317:371–378. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.19975. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

