Image Alignment Based on Deep Learning to Extract Deep Feature Information from Images
- PMID: 40807794
- PMCID: PMC12349225
- DOI: 10.3390/s25154628
Image Alignment Based on Deep Learning to Extract Deep Feature Information from Images
Abstract
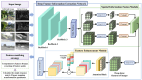
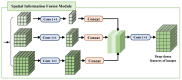
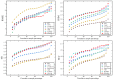
To overcome the limitations of traditional image alignment methods in capturing deep semantic features, a deep feature information image alignment network (DFA-Net) is proposed. This network aims to enhance image alignment performance through multi-level feature learning. DFA-Net is based on the deep residual architecture and introduces spatial pyramid pooling to achieve cross-scalar feature fusion, effectively enhancing the feature's adaptability to scale. A feature enhancement module based on the self-attention mechanism is designed, with key features that exhibit geometric invariance and high discriminative power, achieved through a dynamic weight allocation strategy. This improves the network's robustness to multimodal image deformation. Experiments on two public datasets, MSRS and RoadScene, show that the method performs well in terms of alignment accuracy, with the RMSE metrics being reduced by 0.661 and 0.473, and the SSIM, MI, and NCC improved by 0.155, 0.163, and 0.211; and 0.108, 0.226, and 0.114, respectively, compared with the benchmark model. The visualization results validate the significant improvement in the features' visual quality and confirm the method's advantages in terms of stability and discriminative properties of deep feature extraction.
Keywords: deep learning; feature extraction; image alignment; infrared and visible images.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A novel recursive transformer-based U-Net architecture for enhanced multi-scale medical image segmentation.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Sep;196(Pt A):110658. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.110658. Epub 2025 Jul 6. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40618700
-
A fake news detection model using the integration of multimodal attention mechanism and residual convolutional network.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20544. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05702-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596197 Free PMC article.
-
Structural semantic-guided MR synthesis from PET images via a dual cross-attention mechanism.Med Phys. 2025 Jul;52(7):e17957. doi: 10.1002/mp.17957. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40660837
-
A medical image classification method based on self-regularized adversarial learning.Med Phys. 2024 Nov;51(11):8232-8246. doi: 10.1002/mp.17320. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 39078069
-
A systematic review on feature extraction methods and deep learning models for detection of cancerous lung nodules at an early stage -the recent trends and challenges.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024 Nov 20;11(1). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ad9154. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024. PMID: 39530659
References
-
- Ma J., Jiang X., Fan A., Jiang J., Yan J. Image matching from handcrafted to deep features: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021;129:23–79. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01359-2. - DOI
-
- Jhan J.P., Rau J.Y. A generalized tool for accurate and efficient image registration of UAV multi-lens multispectral cameras by N-SURF matching. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021;14:6353–6362. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3079404. - DOI
-
- Li H., Wu X.J., Kittler J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion. 2021;73:72–86. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.02.023. - DOI
-
- Wang Z., Feng X., Xu G., Wu Y. A robust visible and infrared image matching algorithm for power equipment based on phase congruency and scale-invariant feature. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2023;164:107517. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107517. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

