MB-MSTFNet: A Multi-Band Spatio-Temporal Attention Network for EEG Sensor-Based Emotion Recognition
- PMID: 40807983
- PMCID: PMC12349021
- DOI: 10.3390/s25154819
MB-MSTFNet: A Multi-Band Spatio-Temporal Attention Network for EEG Sensor-Based Emotion Recognition
Abstract
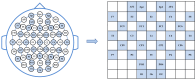
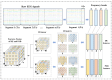
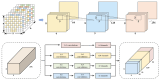
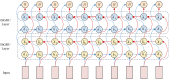
Emotion analysis based on electroencephalogram (EEG) sensors is pivotal for human-machine interaction yet faces key challenges in spatio-temporal feature fusion and cross-band and brain-region integration from multi-channel sensor-derived signals. This paper proposes MB-MSTFNet, a novel framework for EEG emotion recognition. The model constructs a 3D tensor to encode band-space-time correlations of sensor data, explicitly modeling frequency-domain dynamics and spatial distributions of EEG sensors across brain regions. A multi-scale CNN-Inception module extracts hierarchical spatial features via diverse convolutional kernels and pooling operations, capturing localized sensor activations and global brain network interactions. Bi-directional GRUs (BiGRUs) model temporal dependencies in sensor time-series, adept at capturing long-range dynamic patterns. Multi-head self-attention highlights critical time windows and brain regions by assigning adaptive weights to relevant sensor channels, suppressing noise from non-contributory electrodes. Experiments on the DEAP dataset, containing multi-channel EEG sensor recordings, show that MB-MSTFNet achieves 96.80 ± 0.92% valence accuracy, 98.02 ± 0.76% arousal accuracy for binary classification tasks, and 92.85 ± 1.45% accuracy for four-class classification. Ablation studies validate that feature fusion, bidirectional temporal modeling, and multi-scale mechanisms significantly enhance performance by improving feature complementarity. This sensor-driven framework advances affective computing by integrating spatio-temporal dynamics and multi-band interactions of EEG sensor signals, enabling efficient real-time emotion recognition.
Keywords: Inception module; bidirectional gated recurrent unit (BiGRU); convolutional neural network (CNN); electroencephalograph (EEG); emotion signal recognition; multi-head attention (MHA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

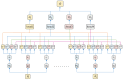
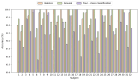
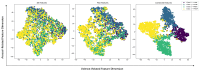
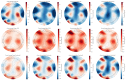

References
-
- Xu W., Jiang H., Liang X. Leveraging Knowledge of Modality Experts for Incomplete Multimodal Learning; Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia; Melbourne, Australia. 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 438–446.
-
- Zhang W., Qiu F., Wang S., Zeng H., Zhang Z., An R., Ma B., Ding Y. Transformer-based multimodal information fusion for facial expression analysis; Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; New Orleans, LA, USA. 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2428–2437.
-
- Zhuang X., Liu F., Hou J., Hao J., Cai X. Transformer-based interactive multi-modal attention network for video sentiment detection. Neural Process. Lett. 2022;54:1943–1960. doi: 10.1007/s11063-021-10713-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

