Multispecies Biofilms Treated With Endodontic Sealers or Calcium Hydroxide: Antimicrobial Activity and Changes in Community Composition
- PMID: 40808237
- PMCID: PMC12518701
- DOI: 10.1111/iej.70015
Multispecies Biofilms Treated With Endodontic Sealers or Calcium Hydroxide: Antimicrobial Activity and Changes in Community Composition
Abstract
Introduction: To evaluate the antimicrobial activity and changes in community composition in biofilms treated with two root canal sealers or calcium hydroxide.
Material and methods: Forty-nine extracted bovine dentine cylinders were inoculated with subgingival dental plaque for 2 weeks in a CDC biofilm reactor. Three treatment groups were assigned: AH Plus, BC Sealer, and calcium hydroxide. Propylene glycol inert vehicle (PG) and untreated contaminated samples were used as controls. The infected root canal space was in direct contact with the materials for 7 days under anaerobic incubation. Anaerobic culture (colony forming units, CFU), quantification PCR (qPCR), and next generation sequencing were used to assess the effect of each material. Differences in the number of molecules (qPCR), CFU, and abundances of genera were evaluated using the Kruskal-Wallis test. The Shannon and Chao1 indices were used to measure alpha diversity. Differences in community composition were evaluated using non-parametric analysis of similarity (ANOSIM).
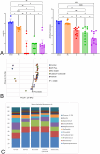
Results: The CFU, Shannon, and Chao1 indices revealed significant differences between BC Sealer, AH Plus, and calcium hydroxide groups versus the untreated control group and PG (p < 0.003). Calcium hydroxide and BC Sealer significantly reduced the qPCR values compared to the control group and PG. The biofilm composition (98.5%) was primarily composed of Peptostreptococcus, Streptococcus, Parvimonas, Fusobacterium, Veillonela, Mogibacterium, Lancefieldella, Eubacterium, Slackia, and Prevotella. Significant differences in overall community composition and beta diversity between untreated controls and AH Plus were observed (ANOSIM R = 0.674, p < 0.001). Parvimonas, Streptococcus, Eubacterium, and Lancefieldella were not affected by any of the materials tested.
Conclusion: Calcium hydroxide and BC Sealer significantly reduced the viability and the total number of DNA copies. AH Plus sealer reduced the bacterial viability but did not affect the DNA concentration. AH Plus significantly alters overall biofilm community composition compared to other groups. None of the materials tested eliminated the multispecies biofilm completely.
Keywords: endodontic sealers; intracanal medication; microbiome; next generation sequencing.
© 2025 The Author(s). International Endodontic Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Endodontic Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alquria, T. A. , Acharya A., Tordik P., Griffin I., and Martinho F. C.. 2024. “Impact of Root Canal Disinfection on the Bacteriome Present in Primary Endodontic Infection: A Next Generation Sequencing Study.” International Endodontic Journal 57: 1124–1135. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, M. J. , and Willis T. J.. 2003. “Canonical Analysis of Principal Coordinates: A Useful Method of Constrained Ordination for Ecology.” Ecology 84: 511–525.
-
- Bray, J. R. , and Curtis J. T.. 1957. “An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin.” Ecological Monographs 27: 325–349.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

