PIRT-Seq: a high-resolution whole-genome assay to identify protein-coding genes
- PMID: 40808296
- PMCID: PMC12350097
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf774
PIRT-Seq: a high-resolution whole-genome assay to identify protein-coding genes
Abstract
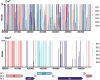
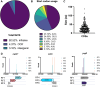
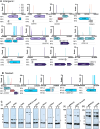
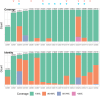
The advent of high-density mutagenesis and data-mining studies suggest the existence of further coding potential within bacterial genomes. Small or overlapping genes are prevalent across all domains of life but are often overlooked for annotation and function because of challenges in their detection. To overcome limitations in existing protein detection methods, we applied a genetics-based approach. We combined transposon insertion sequencing using a dual-selection transposon with a translation reporter to identify translated open reading frames throughout the genome at scale but independent of genome annotation. We applied our method to the well-characterised species Escherichia coli. This method revealed over 200 putative novel protein coding sequences (CDS). These are mostly short CDSs (<50 amino acids) and include proteins that are highly conserved and neighbour functionally important genes. Using chromosomal tags, we validated the expression of selected CDSs. We present this method (Protein Identification through Reporter Transposon-Sequencing: PIRT-Seq) as a complementary method to whole cell proteomics and ribosome trapping for condition-dependent identification of protein CDSs, and as a high-throughput method for testing conditional gene expression. We anticipate this technique will be a starting point for future high-throughput genetics investigations to determine the existence of unannotated genes in multiple bacterial species.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Throwing a spotlight on genomic dark matter: The power and potential of transposon-insertion sequencing.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):110231. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110231. Epub 2025 May 14. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40378959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of essential genes by transposon insertion sequencing and genome-scale metabolic model construction in Streptococcus suis.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 May 6;13(5):e0279124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02791-24. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40162755 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

