SLFN11-mediated tRNA regulation induces cell death by disrupting proteostasis in response to DNA-damaging agents
- PMID: 40808299
- PMCID: PMC12350096
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf789
SLFN11-mediated tRNA regulation induces cell death by disrupting proteostasis in response to DNA-damaging agents
Abstract
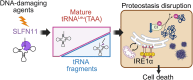
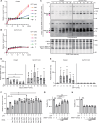
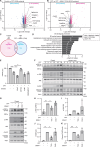
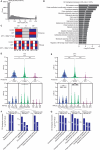
DNA-damaging agents (DDAs) have long been used in cancer therapy. However, the mechanisms by which DDAs induce cell death are not fully understood, and drug resistance remains a major clinical challenge. Schlafen 11 (SLFN11) was identified as the gene most strongly correlated with sensitivity to DDAs based on mRNA expression levels. SLFN11 sensitizes cancer cells to DDAs by cleaving and decreasing tRNALeu(TAA) levels. Elucidating the detailed mechanism by which SLFN11 induces cell death is expected to provide insights into overcoming drug resistance. Here, we show that, upon administration of DDAs, SLFN11 cleaves tRNALeu(TAA), triggering ER stress and protein aggregate formation, leading to cell death regulated by inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha (IRE1α). These responses were significantly alleviated by SLFN11-knockout or transfection of tRNALeu(TAA). Proteomic analysis suggests tRNALeu(TAA) influences proteins essential for maintaining proteostasis, especially those involved in ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Additionally, we identified the cleavage sites of tRNALeu(TAA) generated by SLFN11 in cells and revealed that tRNA fragments contribute to ER stress and cell death. These findings suggest that SLFN11 plays a crucial role in proteostasis by regulating tRNAs and thus determines cell fate under DDA treatment. Consequently, targeting SLFN11-mediated tRNA regulation could offer a novel approach to improve cancer therapy.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Update of
-
SLFN11-mediated tRNA regulation induces cell death by disrupting proteostasis in response to DNA-damaging agents.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 9:2025.01.08.632070. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.08.632070. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Aug 11;53(15):gkaf789. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf789. PMID: 39829761 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

