Integrating Food Preference Profiling, Behavior Change Strategies, and Machine Learning for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in a Personalized Nutrition Digital Health Intervention: Conceptual Pipeline Development and Proof-of-Principle Study
- PMID: 40808315
- PMCID: PMC12346185
- DOI: 10.2196/75106
Integrating Food Preference Profiling, Behavior Change Strategies, and Machine Learning for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in a Personalized Nutrition Digital Health Intervention: Conceptual Pipeline Development and Proof-of-Principle Study
Abstract
Background: Personalized dietary advice needs to consider the individual's health risks as well as specific food preferences, offering healthier options aligned with personal tastes.
Objective: This study aimed to develop a digital health intervention (DHI) that provides personalized nutrition recommendations based on individual food preference profiles (FPP), using data from the UK Biobank.
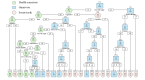
Methods: Data from 61,229 UK Biobank participants were used to develop a conceptual pipeline for a DHIs. The pipeline included three steps: (1) developing a simplified food preference profiling tool, (2) creating a cardiovascular disease (CVD) prediction model using the subsequent profiles, and (3) selecting intervention features. The CVD prediction model was created using 3 different predictor sets (Framingham set, diet set, and FPP set) across 4 machine learning models: logistic regression, linear discriminant analysis, random forest, and support vector machine. Intervention functions were designed using the Behavior Change Wheel, and behavior change techniques were selected for the DHI features.
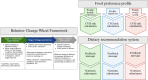
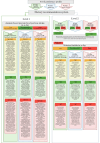
Results: The feature selection process identified 14 food items out of 140 that effectively classify FPPs. The food preference profile prediction set, which did not include blood measurements or detailed nutrient intake, demonstrated comparable accuracy (across the 4 models: 0.721-0.725) to the Framingham set (0.724-0.727) and diet set (0.722-0.725). Linear discriminant analysis was chosen as the best-performing model. Four key features of the DHI were identified: food source and portion information, recipes, a dietary recommendation system, and community exchange platforms. The FPP and CVD risk prediction model serve as inputs for the dietary recommendation system. Two levels of personalized nutrition advice were proposed: level 1-based on food portion intake and FPP; and level 2-based on nutrient intake, FPP, and CVD risk probability.
Conclusions: This study presents proof of principle for a conceptual pipeline for a DHI that empowers users to make informed dietary choices and reduce CVD risk by catering to person-specific needs and preferences. By making healthy eating more accessible and sustainable, the DHI has the potential to significantly impact public health outcomes.
Keywords: UK Biobank; behaviour change; diet; food preference; risk prediction.
©Hana Fitria Navratilova, Anthony David Whetton, Nophar Geifman. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Portion, package or tableware size for changing selection and consumption of food, alcohol and tobacco.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 14;(9):CD011045. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011045.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26368271 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The top 10 causes of death. World Health Organization. 2024. [05-08-2025]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death URL. Accessed.
-
- Goyer L, Dufour R, Janelle C, et al. Randomized controlled trial on the long-term efficacy of a multifaceted, interdisciplinary lifestyle intervention in reducing cardiovascular risk and improving lifestyle in patients at risk of cardiovascular disease. J Behav Med. 2013 Apr;36(2):212–224. doi: 10.1007/s10865-012-9407-3. doi. Medline. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources