Acoustic signatures of bulbar ALS: Predictive modeling with sustained vowels and LightGBM
- PMID: 40808712
- PMCID: PMC12345970
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ensci.2025.100579
Acoustic signatures of bulbar ALS: Predictive modeling with sustained vowels and LightGBM
Abstract
Background: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a degenerative neurologic disease with no definitive biomarkers for early detection. This paper discusses the use of acoustic analysis of sustained vowel phonations (SVP) and machine learning in ALS detection.
Methods: An SVP corpus of 128 (64 /a/ and 64 /i/) from 31 patients with ALS and 33 healthy controls (HC) was employed. 131 acoustic features, including jitter, shimmer, Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs), and Pathological Vibrato Index (PVI), were extracted. A LightGBM (Light Gradient Boosting Machine)-based model was built and optimized using 5-fold cross-validation to separate ALS cases. Model performance and feature importance were evaluated.
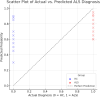
Results: The model performed well with high predictability, yielding an RMSLE of 0.162 and most predictions closely correlating with actual diagnoses. The top features obtained were S55_i, CCI(2), and dCCa(12), which were consistently at the top of the ranking list, indicating their role in ALS detection. The PVI was determined to be a significant biomarker with high values having high correlations with ALS diagnoses. But the multimodal nature of the predictive values indicated some flaws in generalization.
Conclusion: This paper demonstrates the applicability of acoustic analysis and machine learning for early ALS detection. The proposed method provides an affordable, low-cost, and non-invasive way for ALS diagnosis with potential for application in telemedicine and clinical settings. Future research must expand datasets and integrate additional diagnostic modalities to improve the model's robustness and clinical translation.
Keywords: ALS; Acoustic analysis; Feature importance; Machine learning; PVI; SVP.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kent R.D., Kent J.F., Weismer G., Sufit R.L., Rosenbek J.C., Martin R.E., et al. Impairment of speech intelligibility in men with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1990;55(4):721–728. - PubMed
-
- Kent R.D., Weismer G., Kent J.F., Rosenbek J.C. Toward phonetic intelligibility testing in dysarthria. J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1989;54(4):482–499. - PubMed
-
- Duffy J.R. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2012. Motor Speech Disorders: Substrates, Differential Diagnosis, and Management.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

