Integrating air microbiome for comprehensive air quality analysis
- PMID: 40808715
- PMCID: PMC12343473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.113015
Integrating air microbiome for comprehensive air quality analysis
Abstract
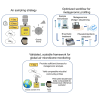
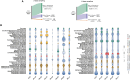
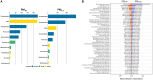
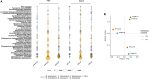
Air quality monitoring typically overlooks the biological composition of airborne particles, despite its relevance to human health. This study evaluated the feasibility of using filters from high-volume air samplers, widely employed in air quality networks, to analyze bioaerosol content through shotgun metagenomic sequencing. We developed a DNA extraction method for ultra-low biomass samples and assessed the impact of sampling duration, particle size selection, and filter material on microbial diversity. Our findings show that prolonged continuous sampling reduces species detection, while larger particle size selectors capture a broader range of microbial content, particularly fungi. Comparisons with a dedicated bioaerosol sampler confirmed that these filters can yield comparable results. This work demonstrates that existing air quality infrastructure can be leveraged for airborne microbiome monitoring, offering a practical and cost-effective approach to integrate biological data into routine assessments and support a more comprehensive understanding of air quality and its implications for public health.
Keywords: Environmental monitoring; Microbiology; Microbiome.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
An Optimized Active Sampling Procedure for Aerobiological DNA Studies.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 5;23(5):2836. doi: 10.3390/s23052836. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36905039 Free PMC article.
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
Individual-level interventions to reduce personal exposure to outdoor air pollution and their effects on people with long-term respiratory conditions.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 9;8(8):CD013441. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013441.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34368949 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that influence caregivers' and adolescents' views and practices regarding human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination for adolescents: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 15;4(4):CD013430. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013430.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40232221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hou J., Fujiyoshi S., Perera I.U., Nishiuchi Y., Nakajima M., Ogura D., Yarimizu K., Maruyama F. Perspectives on Sampling and New Generation Sequencing Methods for Low-Biomass Bioaerosols in Atmospheric Environments. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2023;103:687–697. doi: 10.1007/s41745-023-00380-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

