Tissue specific role of ABCA1 in lung cholesterol homeostasis under high-cholesterol diet
- PMID: 40808841
- PMCID: PMC12343695
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1649407
Tissue specific role of ABCA1 in lung cholesterol homeostasis under high-cholesterol diet
Abstract
Background: ATP-binding cassette subfamily A1 (ABCA1) and sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) are essential regulators of cholesterol metabolism. However, their tissue-specific roles, particularly in the lung, under high-cholesterol diet (HCD) conditions remain unclear.
Objective: Using the liver as a reference, this study aimed to investigate the tissue-specific regulation of ABCA1 in the lung under HCD or CYP27A1 knockout (KO) conditions, and to explore its potential regulatory mechanism.
Methods: CYP27A1 KO and wild-type (WT) mice on a C57BL/6J background were fed either a normal diet (ND) or HCD for 12 weeks. Transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) was conducted on lung tissue samples.
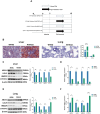
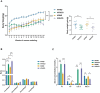
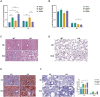
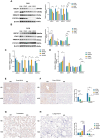
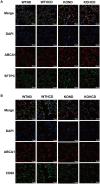
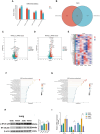
Results: HCD feeding in WT mice caused significant hepatic lipid accumulation, while no notable lipid deposition was observed in lung tissue. ABCA1 and CYP27A1 expression were downregulated in the liver but upregulated in the lung. In CYP27A1 (-/-) mice, hepatic lipid accumulation was more severe with further suppression of ABCA1, whereas ABCA1 expression in the lung remained elevated. Transcriptome analysis revealed that upregulated genes in lung tissue were significantly enriched in the inflammation-related nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathway. Furthermore, experiments confirmed that the expression of NF-κB pathway was consistent with the upregulation of ABCA1.
Conclusion: ABCA1 exhibits marked tissue specificity under HCD feeding or CYP27A1 KO conditions. In the liver, ABCA1 downregulation may exacerbate cholesterol metabolic imbalance, while its upregulation in the lung may play an important role in maintaining cholesterol homeostasis. Moreover, the increase in pulmonary ABCA1 expression in CYP27A1 KO mice may be associated with activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: ABCA1; cholesterol homeostasis; high-cholesterol diet; lung metabolism; tissue specificity.
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Gong, Lu, Yang, Wang, Zhu, Liu, Li, Zhang and Lian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ertugliflozin attenuates atherosclerosis in nondiabetic ApoE-/- mice by upregulating ABCA1 and LDLR via the PPARγ/LXRα pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025 Oct;1871(7):167927. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2025.167927. Epub 2025 May 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025. PMID: 40419168
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Injinoryeong-San attenuates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis via regulation of YAP/TAZ-signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 17;353(Pt A):120292. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120292. Online ahead of print. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40683423
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

